Table 3.
Contribution of Amino Acid Side-Chains to Stability in the Hydrophobic Core of α-Helical Coiled-Coils3
Amino acid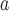
|
ΔΔGu (Ala)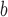 (position a) (position a) |
ΔΔGu (Ala)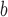 (position d) (position d) |
|---|---|---|
| Val | 4.1 | 1.1 |
| Ile | 3.9 | 3.0 |
| Leu | 3.5 | 3.8 |
| Met | 3.4 | 3.2 |
| Phe | 3.0 | 1.2 |
| Tyr | 2.2 | 1.4 |
| Asn | 0.9 | -0.6 |
| Trp | 0.8 | -0.1 |
| Thr | 0.2 | -1.2 |
| Ala | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Gln | -0.1 | 0.5 |
| Lys | -0.4 | -1.8 |
| Arg | -0.8 | -2.9 |
| His | -1.2 | -0.8 |
| Ser | -1.3 | -1.8 |
| Orn | -1.9 | -3.1 |
| Glu | -2.0 | -2.7 |
| Gly | -2.5 | -3.6 |
| Asp | -c | -1.8 |
 Amino acid residue (denoted X) substituted at position 19a of the sequence Ac-CGGEVGALKAQVGALQAQXGALQKEVGALKKEVGA LKK-amide or at position 22d of the sequence Ac-CGGEVGALKAEVGAL KAQIGAXQKQIGALQKEVGALKK-amide; oxidation of the peptides formed a disulfide-bridged homo-two-stranded α-helical coiled-coil.
Amino acid residue (denoted X) substituted at position 19a of the sequence Ac-CGGEVGALKAQVGALQAQXGALQKEVGALKKEVGA LKK-amide or at position 22d of the sequence Ac-CGGEVGALKAEVGAL KAQIGAXQKQIGALQKEVGALKK-amide; oxidation of the peptides formed a disulfide-bridged homo-two-stranded α-helical coiled-coil.
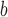 ΔΔGu (Ala) is the difference in the free energy of unfolding (ΔGu) relative to the Ala-substituted analog; a positive value indicates the substitution provides more stability relative to Ala; a negative value indicates the substitution is destabilizing relative to Ala.
ΔΔGu (Ala) is the difference in the free energy of unfolding (ΔGu) relative to the Ala-substituted analog; a positive value indicates the substitution provides more stability relative to Ala; a negative value indicates the substitution is destabilizing relative to Ala.
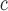 A value for the Asp side-chain could not be obtained as a result of its causing unfolding of the coiled-coil, i.e., it is more destabilizing than Gly.
A value for the Asp side-chain could not be obtained as a result of its causing unfolding of the coiled-coil, i.e., it is more destabilizing than Gly.
