Fig. 1.2.
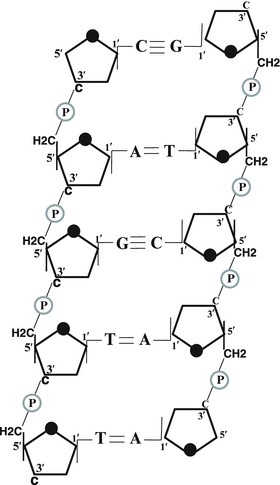
The double helical structure of DNA where both strands are running in opposite direction. Elongation of the chain occurs due to formation of phosphodiester bond between phosphate at 5′ and hydroxyl group of sugar at 3′ of the adjacent sugar of the nucleotide in 5–3′ direction. The sugar is attached to the base. Bases are of four kinds: adenine (A), guanine (G) (purines), thymine (T), and cytosine (C) (pyrimidines). Adenine base pairs with two hydrogen bonds with thymine on the opposite antiparallel strand and guanine base pairs with three hydrogen bonds with cytosine present on the opposite antiparallel strand
