Fig. 11.2.
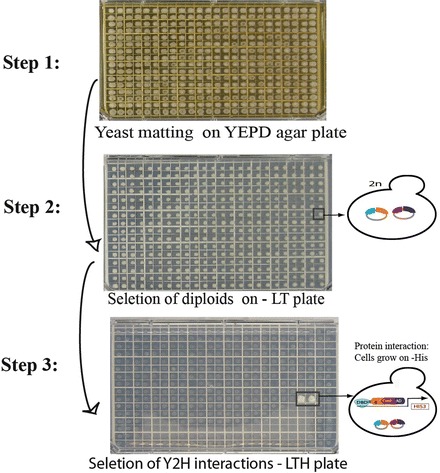
Array-based yeast two-hybrid screens. Step 1: Yeast mating combines the bait and prey plasmids. The bait (DNA-binding domain (DBD) fusion) liquid culture is pinned onto YEPDA agar plates using a 384-pin pinning tool, and then the prey array (activation-domain (AD) fusion) is pinned on top of the baits using the sterile pinning tool. The mating plates are incubated at 30 °C for 16 h. Step 2: The cells from the yeast mating plates are transferred onto –Leu –Trp medium plates using a sterile 384-pin pinning tool. Only diploid cells will grow on the media lacking leucine and tryptophan agar plates and ensures that both the prey and bait plasmids are combined in the diploid yeast cells. Step 3: The diploid cells are transferred onto –Leu –Trp –His medium plates for protein interaction detection. If the bait and prey proteins interact, and an active transcription factor is reconstituted and transcription of a reporter gene is activated. Thus, the cells can grow on selective media plates
