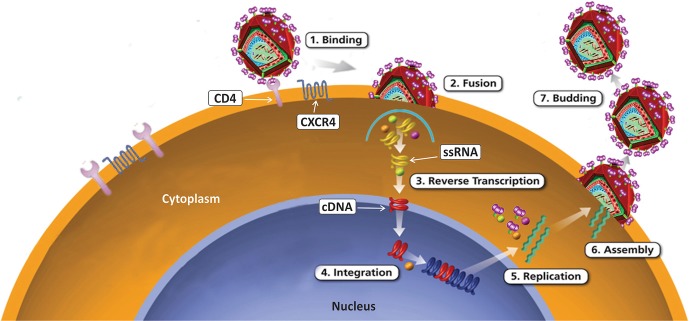
Fig. 7.2.
HIV Replication
Schematic representation of different step of HIV replication. During infections, HIV attaches to the CD4 receptor on cell surface of target cells permissive for HIV. After attachment, HIV fuses with the cell membrane of target cells. HIV RNA and other proteins are released inside the target cell after attachment and fusion of HIV with plasma membrane. After activation, reverse transcriptase enzyme produces pro-viral DNA in cytoplasm. Now pro-viral DNA moves to the nucleus and gets integrated with the genome of host cells with the help of integrase enzyme of HIV. After integration to the host cell genome, pro-viral DNA produces mRNA. Newly synthesized viral mRNA translates into different types of viral proteins necessary for the production of new virions. Viral proteases cleave these proteins for the assembly of new virions. These new virions are released into host circulation from the infected cells, Viral RNA; pro-viral DNA