Fig. 3.
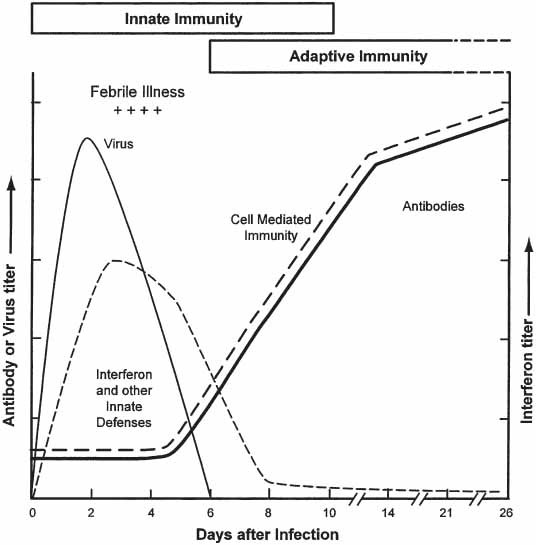
The roles of innate and adaptive immunity during acute influenza virus infection of humans. During virus infection, the earliest defenses are innate. They include interferon, anatomic barriers, nonspecific inhibitors, phagocytosis, fever, and inflammation. The innate defenses begin within hours and continue until virus is eliminated. The adaptive defenses are specific antibody and cell-mediated immunity. They begin within 5 to 7 d of infection and persist for months after virus is eliminated. Virus levels initially increase rapidly, begin to decline in the presence of the innate defenses, and virus is eliminated after the development of the adaptive defenses. Adapted from ref. 4.
