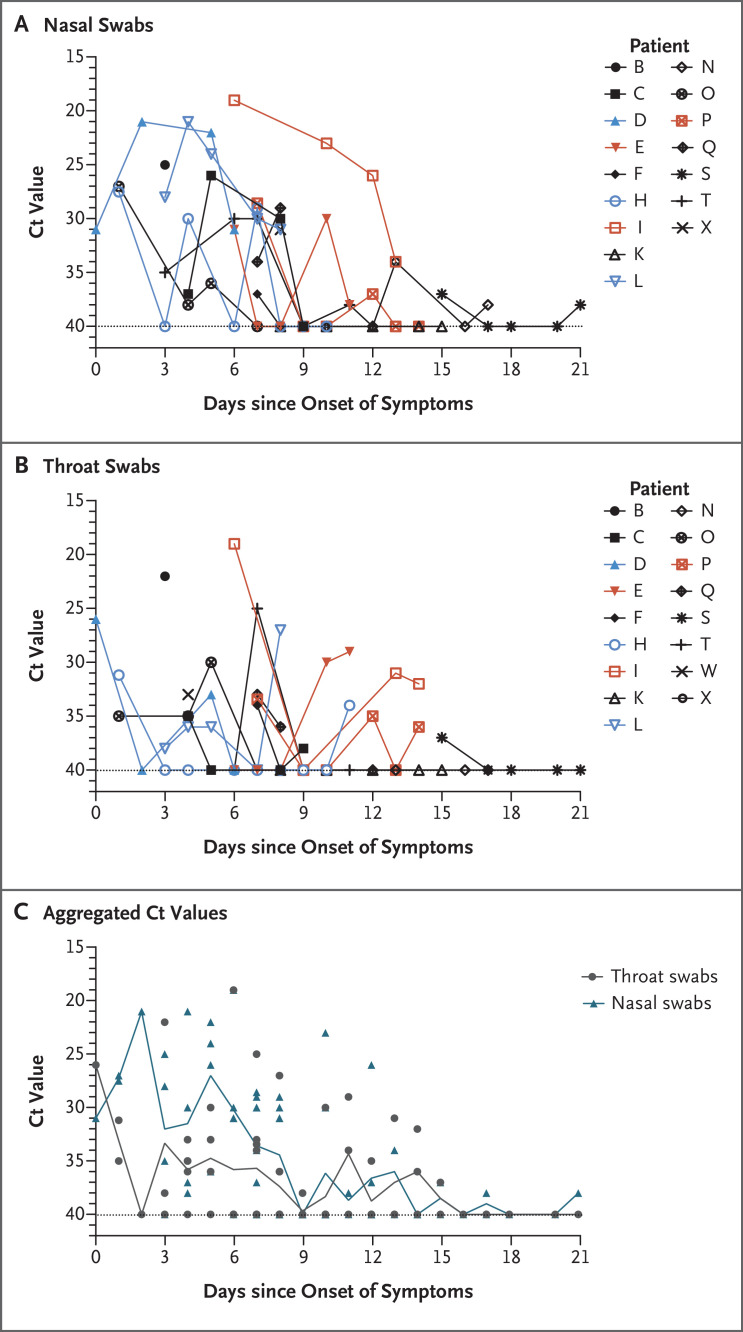
Figure 1. Viral Load Detected in Nasal and Throat Swabs Obtained from Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Panel A shows cycle threshold (Ct) values of Orf1b on reverse-transcriptase–polymerase-chain-reaction (RT-PCR) assay that were detected in nasal swabs obtained from 14 patients with imported cases and 3 patients with secondary cases, and Panel B shows the Ct values in throat swabs. Patient Z did not have clinical symptoms and is not included in the figure. Patients with imported cases who had severe illness (Patients E, I, and P) are labeled in red, patients with imported cases who had mild-to-moderate illness are labeled in black, and patients with secondary cases (Patients D, H, and L) are labeled in blue. A linear mixed-effects model was used to test the Ct values from nasal and throat swabs among severe as compared with mild-to-moderate imported cases, which allowed for within-patient correlation and a time trend of Ct change. The mean Ct values in nasal and throat swabs obtained from patients with severe cases were lower by 2.8 (95% confidence interval [CI], −2.4 to 8.0) and 2.5 (95% CI, −0.8 to 5.7), respectively, than the values in swabs obtained from patients with mild-to-moderate cases. Panel C shows the aggregated Ct values of Orf1b on RT-PCR assay in 14 patients with imported cases and 3 patients with secondary cases, according to day after symptom onset. Ct values are inversely related to viral RNA copy number, with Ct values of 30.76, 27.67, 24.56, and 21.48 corresponding to 1.5×104, 1.5×105, 1.5×106, and 1.5×107 copies per milliliter. Negative samples are denoted with a Ct of 40, which was the limit of detection.