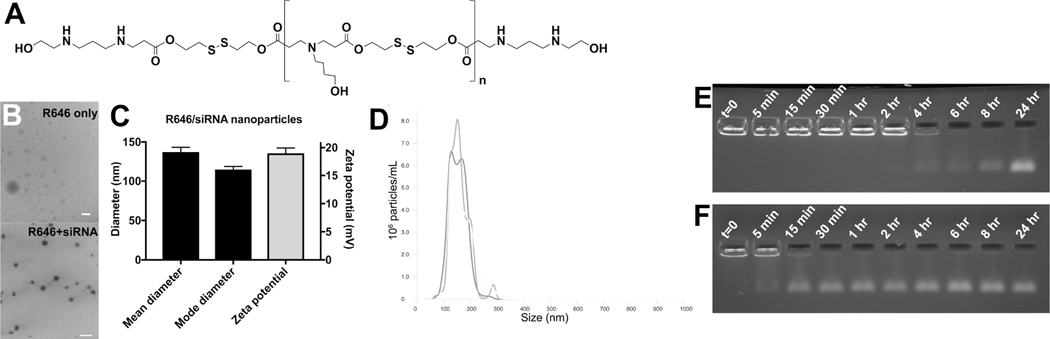
Figure 1. Physicochemical characterization of R646/siRNA nanoparticles.
siRNA-containing nanoparticles (NPs) based on (A) polymer structure R646 are of (B) Spherical morphology, (C) Small ~100 nm size, and have positive zeta potential. (D) Particle size distribution of the self-assembled R646 siRNA NPs is approximately monodisperse. Gel retention assay results of siRNA release from NPs over time show (E) Persistence of the NPs over longer times in aCSF, mimicking the extracellular space, compared to (F) Faster release of siRNA from the NPs in conditions mimicking the cytosol with 5 mM GSH. Scale bars = 200 nm.