Fig. 1.
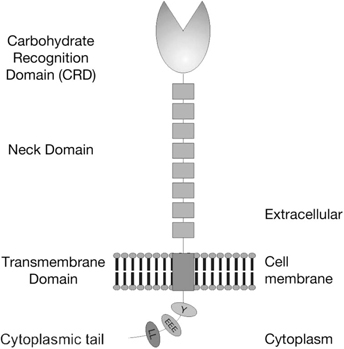
Structure of DC-SIGN and L-SIGN proteins. The C-type lectins DC-SIGN and L-SIGN are type II transmembrane proteins. Their cytoplasmic tails contain internalization signals (di-leucine, tyrosine, and tri-acidic) which are involved in internalization of the lectin. The extracellular domain is composed of a carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD) and a neck domain (conserved in the case of DC-SIGN, variable for L-SIGN) implicated in the oligomerization of these lectins. The oligomerization is probably important for the orientation and subsequently for the function of the CRDs.
