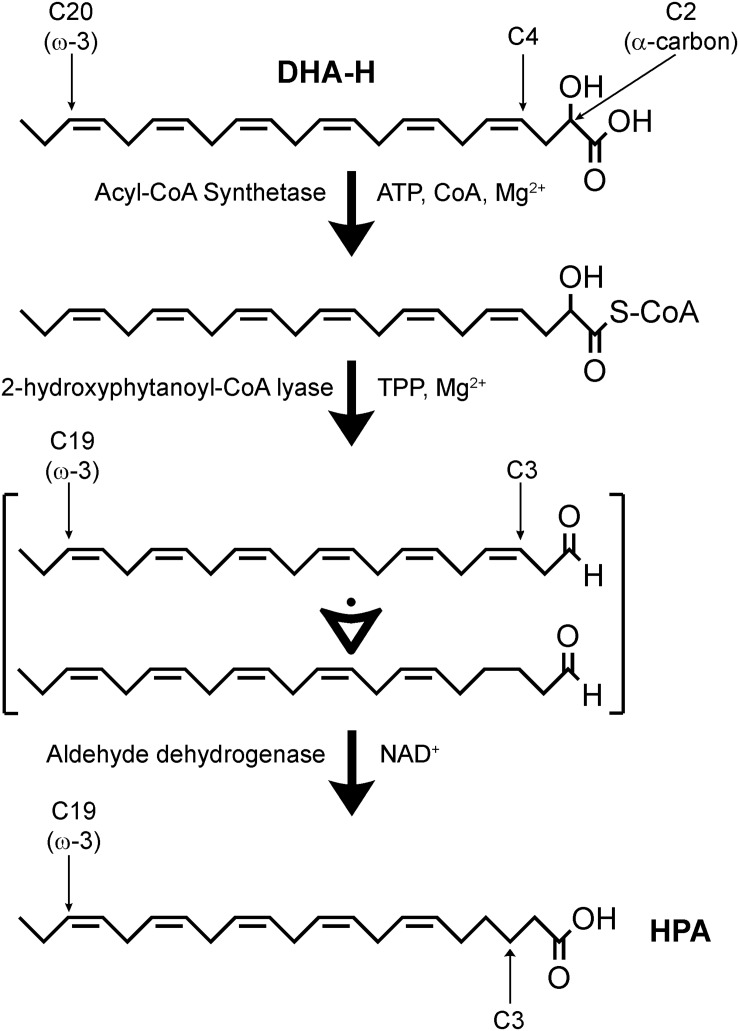
FIGURE 2.
Hypothetic α-oxidation pathway for the conversion of DHA-H into HPA. DHA-H requires activation by an acyl-CoA synthetase. DHA-H-CoA would be subject to 2-hydroxyphytanoyl-CoA lyase (HACL1) activity, leading to the formation of an intermediate polyunsaturated fatty aldehyde which should contain 5 or 6 double bonds. It is not clear at what time the double bond originally located at DHA-H carbon 4 is lost. This process is dependent on thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) and Mg2+, and it can be inhibited by the competitive antagonist, oxythiamine. Aldehyde dehydrogenase would be responsible for conversion of the intermediate aldehyde into HPA and the subsequent metabolism of HPA would take place via β-oxidation.