Fig. 22.7.
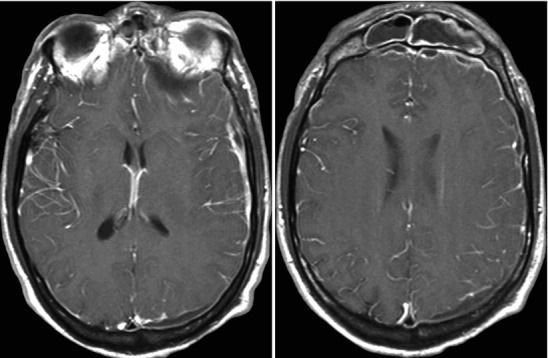
Acute frontal sinusitis with secondary subdural empyema; images include contiguous post-contrast mid-convexity axial MRI sections. This case illustrates the spread pattern of subdural empyema. The source of the infection is the frontal sinus. Once the infection accesses the subdural space it can spread widely within the intracranial compartment. In this instance, it continues all the way to the occipital region. These multicentric pockets of subdural empyema are often sequestered requiring multiple surgical drains. Thus, it is imperative that the full extent of the subdural empyema is appreciated
