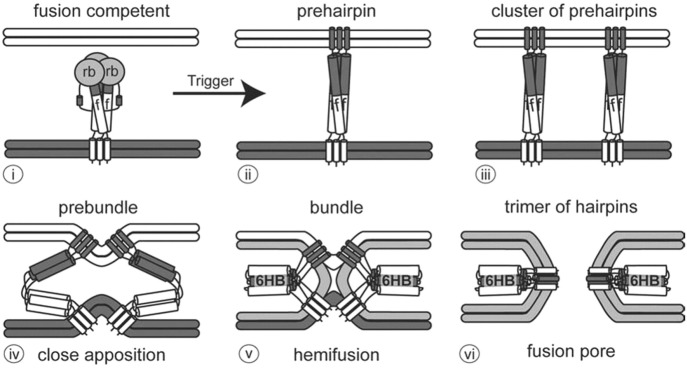
Fig. 2.2.
Steps in viral fusion. (i) The viral envelope (bottom) approaches the target membrane (top). The viral fusion protein consists of a receptor binding domain (rb) and a fusion domain (f). (ii) The prehairpin structure embeds into the target membrane. (iii) Several prehairpin trimers cluster together. (iv) The prehairpins begin to fold back to form the prebundle state and bring the membranes close together. (v) Fusion proteins further fold into a six helix bundle (6HB). Lipids in the outer leaflets of the viral and target bilayers mix during hemifusion. (vi) A pore opens between the target membrane and the viral envelope as the fusion proteins become a trimer of hairpins. Source: White et al. [5], Taylor & Francis Ltd., www.tandfonline.com