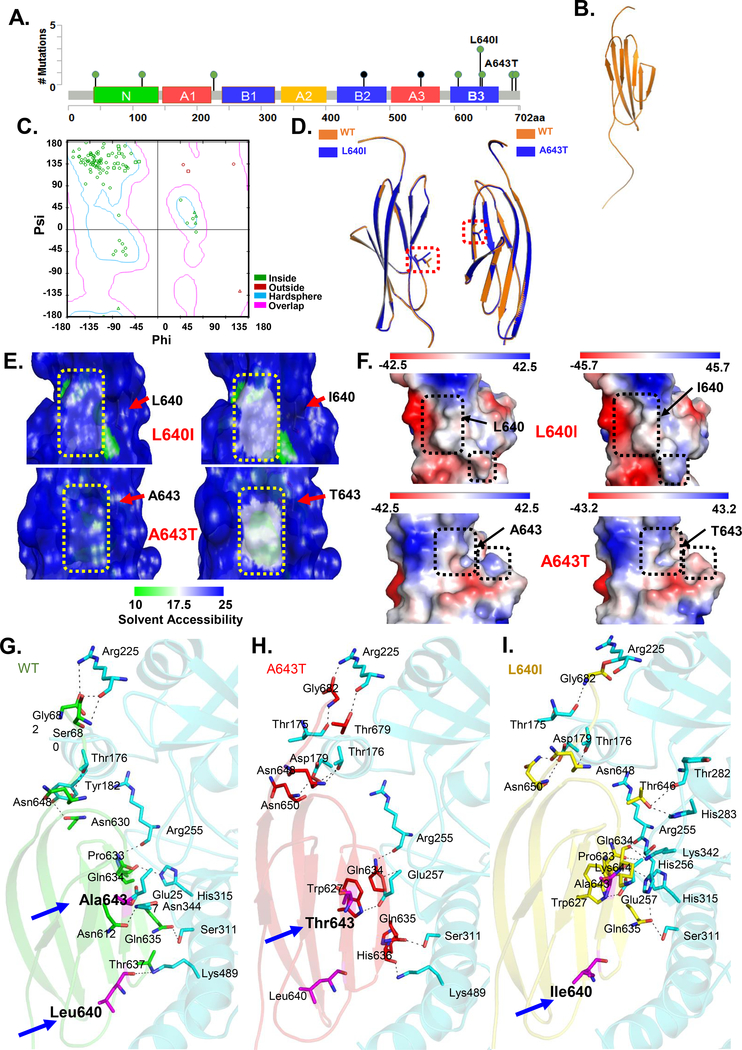
Figure 4.
Structure of CEACAM5 hotspot mutants in the B3 domain. A) Diagram of CEACAM5 point mutations in CRC from cBioportal with the 2 newly identified mutations indicated. B) Predicted 3-D model of CEACAM5 B3 domain. C) Ramachandran plot for predicted model generated using Discovery studio visualizer. D) Overlay of the predicted structures of the B3 domains of each mutant with the wild-type (WT). E) Predicted changes in solvent accessibility (SAS) of B3 domain WT and mutant at position 640 (top) and WT and mutant at position 643 (bottom). Arrow shows the region of change. F) Predicted changes in electrostatic potential of B3 domain wildtype and mutant at position 640 (top) and wild-type and mutant at position 643 (bottom). Arrow shows the region of change in electrostatic potential. G-I) Predicted interactions between WT CEACAM5 or mutant CEACAM5 B3 domains (L640I and A643T) and TGFBR1. Arrows indicate the positions of the mutated residues L640I and A643T.