Fig. 19.
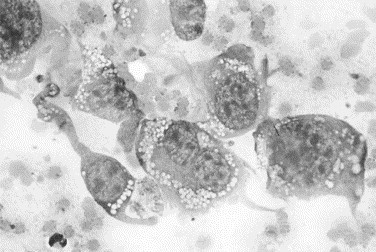
Canine joint fluid. This joint was hot, painful, and swollen, with radiographic evidence of osteolysis. The fluid is hemorrhagic and contains neutrophils and mononuclear cells. A second population of cells exhibiting marked variation in cell size and shape, variable nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratios, variation in nuclear size, and extremely variable nucleolar size and shape is visible. These cells are consistent with a malignancy of connective tissue origin. The histologic diagnosis was synovial cell sarcoma (Wright stain, original magnification ×1000).
