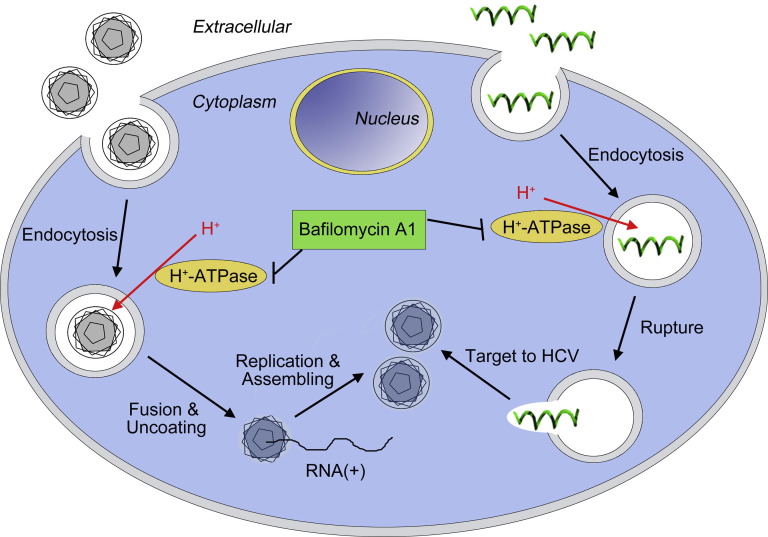
Fig. 10.
Schematic diagram illustrating a mechanism of the histidine-rich peptide action via the cellular uptake and endosomal escape pathways. The peptides were taken up by the cells via endocytosis and were restricted in endosomes. With the acidification of endosomes by H+-ATPase, common peptides would be digested by the enzyme, whereas Ctry2459-H2 and Ctry2459-H3 with endosomal escape properties can easily break through the endosomal barrier. The released peptides in the cytoplasm would be targeted to intracellular HCV particles and act as an antiviral compound.