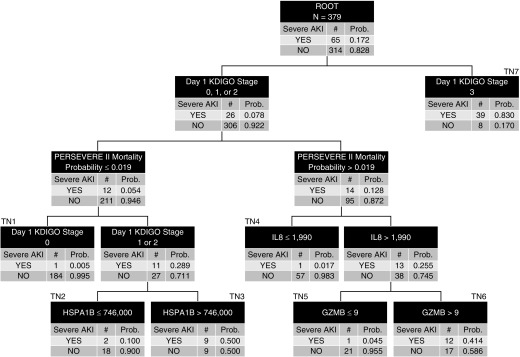
Figure 2.
The derived decision tree for estimating the risk of severe sepsis-associated acute kidney injury on Day 3 (D3 SA-AKI). All patients (n = 379) are included in the root node at the top of the tree, with the corresponding number of those with and without D3 SA-AKI and the respective rates. Patients were subsequently allocated to daughter nodes using decision rules, as indicated in the top row of each node. All biomarker data are shown as pg/ml. Each daughter node provides the number of patients with and without D3 SA-AKI and the respective rates. Subsequent daughter nodes were generated, ending in terminal nodes (TNs). The TNs are used to assign the risk of D3 SA-AKI to a patient classified to a given TN, which is used for construction of the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve. For calculation of the diagnostic test characteristics, the D3 SA-AKI risk is dichotomized into those who are predicted to not have D3 SA-AKI and those who are predicted to have D3 SA-AKI. Patients allocated to TN1, TN2, TN4, and TN5 (D3 SA-AKI risk, 0.005–0.100) were classified as predicted to not have D3 SA-AKI. Patients allocated to TN3, TN6, and TN7 (D3 SA-AKI risk, 0.414–0.830) were predicted to have D3 SA-AKI. GZMB = granzyme B; HSPA1B = heat shock protein 70 kD 1B; KDIGO = Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes; PERSEVERE-II = updated Pediatric Sepsis Biomarker Risk Model; Prob. = probability.