Figure 6.
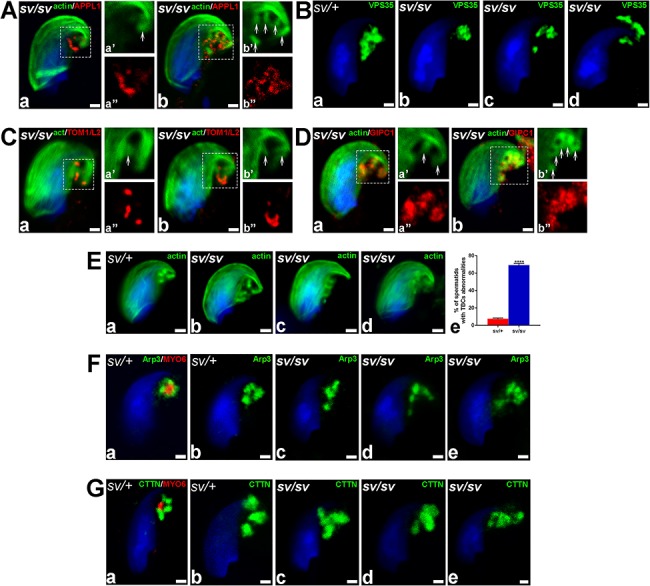
Lack of MYO6 in sv/sv spermatids leads to the dispersion of TBC endocytic compartment. (A) Confocal microscope images of stage VII sv/sv spermatids immunostained for APPL1 (red) and F-actin (green). (B) Confocal microscope images of stage VII sv/+ and sv/sv spermatids immunostained for VPS35 (green). (C) Confocal microscope images of stage VII sv/sv spermatids immunostained for TOM1/L2 (red) and F-actin (green). (D) Confocal microscope images of stage VII sv/sv spermatids immunostained for GIPC1 (red) and F-actin (green). (E) Confocal microscope images of stage VII sv/+ and sv/sv spermatids stained for F-actin (green) (a–d). The graph depicting the mean percentage of cells which displayed disturbed TBC-associated cytoskeleton (e). > 90 cells from n = 3 independent experiments were counted (3 litter pairs of sv/+ and sv/sv males). Error bars indicate SEM, ****P ≤ 0.0001. (F) Confocal microscope images of stage VII sv/+ and sv/sv spermatids immunostained for MYO6 (a, red) and Arp3 (a–e, green). (G) Confocal microscope images of stage VII sv/+ and sv/sv maturing spermatids immunostained for MYO6 (a, red) and cortactin (a–e, green). Arrows highlight the position of TBCs and dotted squares indicate areas magnified in images marked with prime and double prime. All bars 1 μm.
