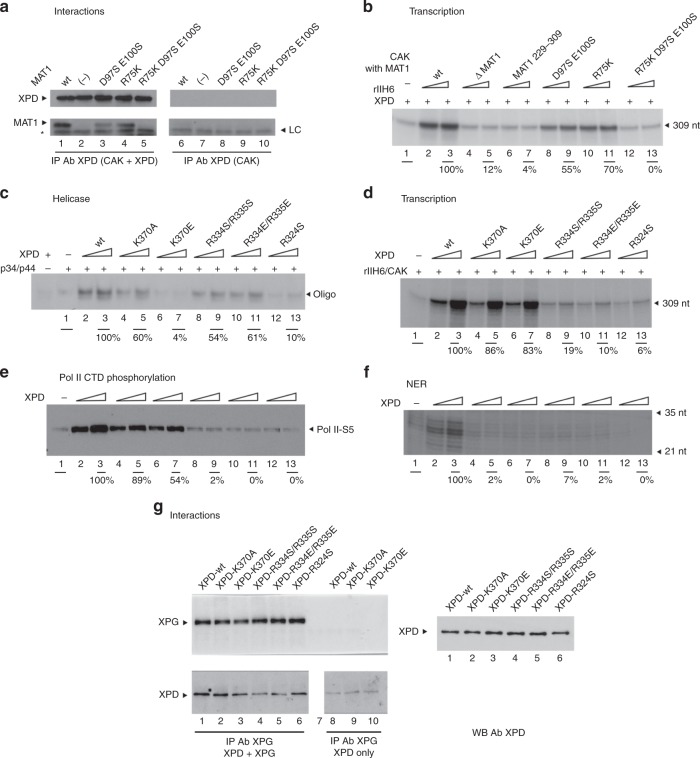
Fig. 5. Functional analysis of human XPD and MAT1 variants.
a XPD/CAK interactions analyzed using a pull-down assay with immobilized XPD (Lanes 1–5). Control extract (for details see Method section; lanes 6–10). MAT1 and XPD were detected using specific antibodies. The asterisk marks the light chain of the antibody (LC). b In vitro transcription activity assay of wild-type MAT1 and its variants. Purified CAK lacking MAT1 (∆ MAT1) or containing its variants (100 and 250 ng) were added to a reconstituted system containing core-TFIIH lacking XPD (rIIH6) (250 ng) and XPD (200 ng). Transcripts were analyzed by electrophoresis followed by autoradiography (309 nt run-off transcript) and was normalized to that of wild-type CAK/MAT1. Numbers correspond to the average values obtained for the two quantities of CAK tested. c XPD Helicase assay. Increasing amounts of XPD wild type and variants (100 and 200 ng) were added to a 5′-strand extension probe (for details see Method section; lanes 2–13). Controls were performed in absence of p34/p44 or XPD as indicated. The reaction was analyzed by electrophoresis followed by autoradiography and helicase activity (unwound oligonucleotide, black arrow) was normalized to that of wild-type XPD. The average activity estimated from three independent experiments (n = 3, mean, ±sd) using the highest XPD concentration is indicated in Table 3, whereas the panel shows a representative experiment. d In vitro transcription activities of reconstituted TFIIH containing XPD variants (see Methods section for details). The size of the transcript is indicated by the black arrow and the transcription activity estimated using the highest XPD concentration is indicated below the autoradiography. The average activity estimated from four independent experiments (two independent sets of reactions performed with the two XPD concentrations, n = 4, mean ± sd) is indicated in Table 3, whereas the panel shows a representative experiment. Lane labels of c and d apply also to e and f, respectively. e Phosphorylation activities of the TFIIH complexes analyzed by immunoblotting using an antibody directed against the phosphorylated form of serine 5 from the CTD heptad repeat. f In vitro NER activity of reconstituted TFIIH containing XPD variants. XPD wild type or variants (100 and 200 ng, see Method section for details). The NER product is visible between the 35 and 21 nt limits. g Pull-down assay with XPG and wild-type XPD as well as XPD variants. Lanes 1–6 present the pulldown experiments where XPG was immobilized with an anti-XPG antibody. For control experiments an extract expressing the DsRed protein instead of human XPG was used (lanes 8–10). XPD and XPG were detected by Western Blot using monoclonal antibodies. The XPD loading controls of lanes 1–6 are shown on the right side of the panel.