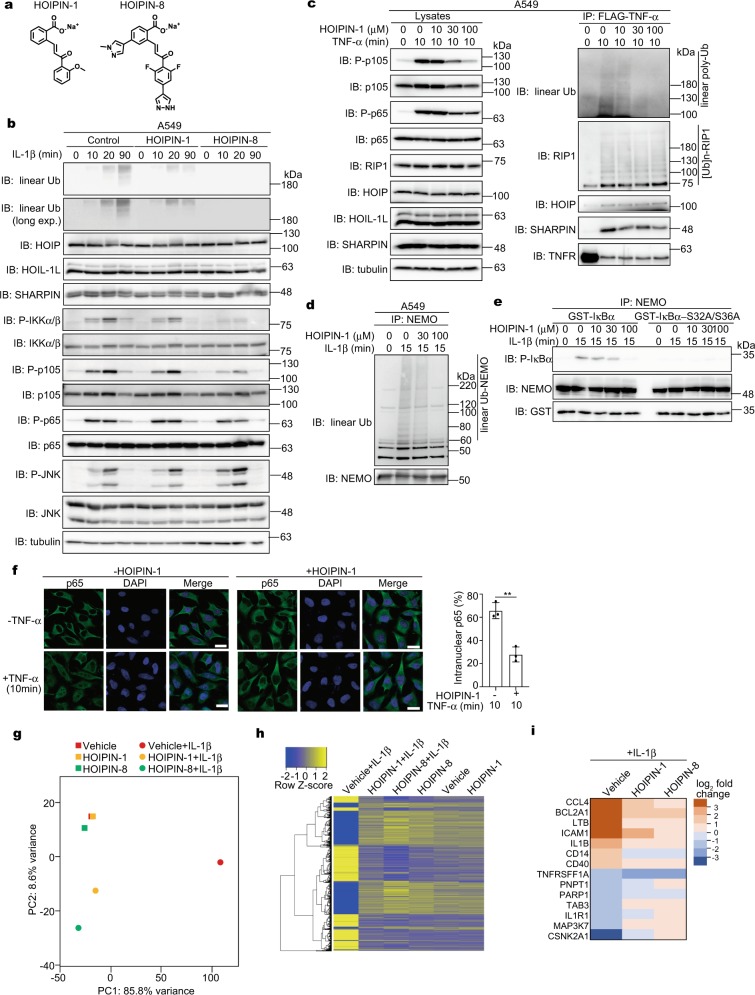
Fig. 1. HOIPINs inhibit inflammatory cytokine-induced NF-κB activation.
a Chemical structures of HOIPIN-1 and HOIPIN-8. b IL-1β-induced NF-κB activation are suppressed by HOIPINs. A549 cells were pre-treated with 30 μM HOIPIN-1 or HOIPIN-8 for 30 min, and then stimulated with 1 ng/ml IL-1β with HOIPINs for the indicated period. After SDS-PAGE, cell lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. c TNFR complex I formation is not suppressed by HOIPIN-1. A549 cells were pre-treated with the indicated concentrations of HOIPIN-1 for 30 min, and stimulated with 1 μg/ml FLAG-TNF-α and HOIPIN-1 for 10 min. Cell lysates and anti-FLAG immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. d Suppression of IL-1β-induced linear ubiquitination of NEMO in the presence of HOIPIN-1. A549 cells were pre-treated with the indicated concentrations of HOIPIN-1 for 3 h, and stimulated with 1 ng/ml IL-1β with HOIPIN-1. After heat denaturation, the endogenous NEMO was immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. e Reduced canonical IKK activity by HOIPIN-1. A549 cells were pre-treated with the indicated concentrations of HOIPIN-1, and stimulated with 1 ng/ml IL-1β and HOIPIN-1 for 15 min, and then NEMO was immunoprecipitated. The in vitro IKK activity was assessed using GST-IκBα or its Ser32 → Ala/Ser36 → Ala mutant as substrates. f TNF-α-induced nuclear translocation of p65 is retarded by HOIPIN-1. HeLa cells were pre-treated with or without 100 μM HOIPIN-1 for 30 min, and stimulated with 20 ng/ml TNF-α for 10 min. Immunofluorescent staining of p65 and nuclear staining were analyzed, and intranuclear p65 was counted. Bars, 20 μm. Data are shown as mean ± SEM, n = 3, NS not significant, **P < 0.01, Student’s t-test. g–i The IL-1β-induced gene expression in A549 cells was canceled by HOIPINs. A549 cells were pre-treated with 100 μM HOIPIN-1 or 30 μM HOIPIN-8 for 2 h, and stimulated with 1 ng/ml IL-1β for 2 h. The cells were lysed, and subjected to transcriptome-wide expression using their extracted total RNA. A principal component analysis of the RNA-seq analysis (g), the heatmaps of the gene expression in the inflammatory pathway (h), and the major genes in the NF-κB signal affected by HOIPINs (i) are shown.