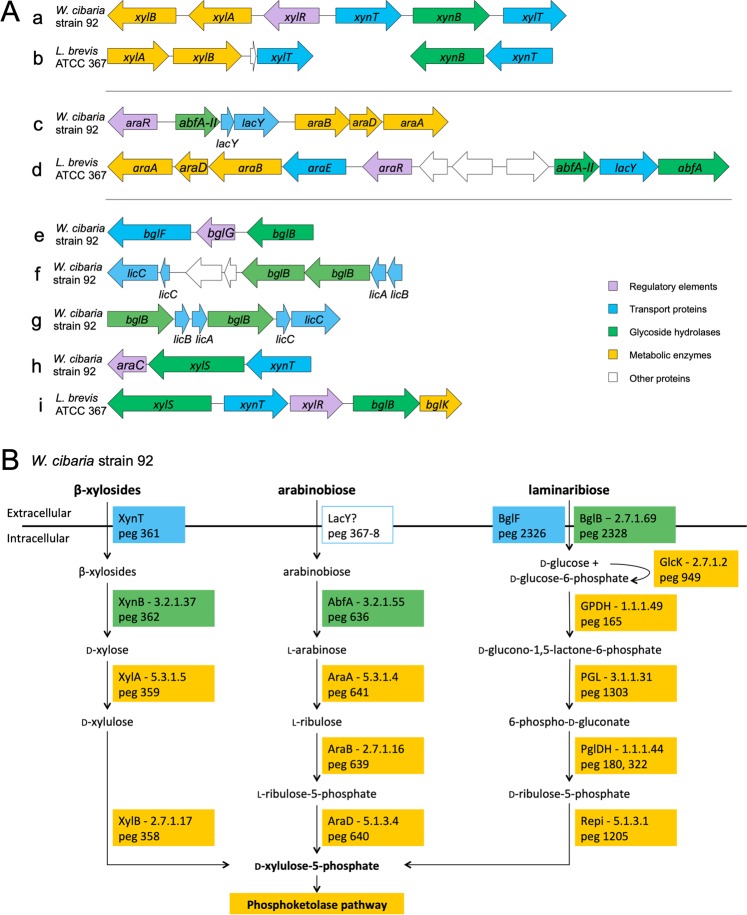
Figure 3.
(A) Organisation of gene clusters in Weissella cibaria strain 92 and Lactobacillus brevis ATCC 367 involved in regulation, transport, degradation and metabolism of β-xylosides (a,b), α-l-arabinosides (c,d) and β-glucosides (e-i) including cellobiose (f-g) and α-xyloglucosides (h-i). The clusters correspond to protein encoding gene (peg) 358–363 (a), 635–641 (c), 2326–2328 (e), 298–305 (f), 1258–1263 (g) and 215–217 (h) of W. cibaria strain 92 annotation, and LVIS_183–186 and LVIS_2285–2286 (b), LVIS_1740–1750 (d) and LVIS_462–466 (i) of L. brevis ATCC 367. The genes are annotated to encode the following proteins; xylB – xylulose kinase, xylA – xylose isomerase, xylR – putative ROK family transcriptional regulator, xynT – xyloside transporter, xynB – β-xylosidase, xylT – d-xylose proton symporter, araR – transcriptional repressor of arabinoside utilisation operon, GntR family, abfA-II – α-l-arabinofuranosidase II precursor, lacY – lactose permease, araB – ribulokinase, araD – l-ribulose-5-phosphate-4-epimerase, araA – l-arabinose isomerase, araE – arabinose proton symporter, abfA – α-l-arabinofuranosidase, bglF – PTS, β-glucoside-specific II(A–C) component, bglG - β-glucoside bgl antiterminator bgl family, bglB – 6-phospho-β-glucosidase, licA-C – PTS cellobiose-specific IIA-C component, araC – transcriptor regulator, AraC family, xylS – α-xylosidase and bglK – sugar kinase (34% identity with β-glucoside kinase from Klebsiella pneumoniae (Uniprot Q39LQ8)). (B) Pathways for utilisation of β-xylosides, arabinobiose and laminaribiose based on protein activities (EC numbering) annotated within W. cibaria strain 92. GlcK - glucokinase, GPDH - glucose-6-phosphate 1-dehydrogenase, PGL - 6-phosphogluconolactonase, PglDH - 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, decarboxylating, Repi - ribulose-phosphate 3-epimerase.