Fig. 5. Azidothymidine rescues tigecycline activity in vivo.
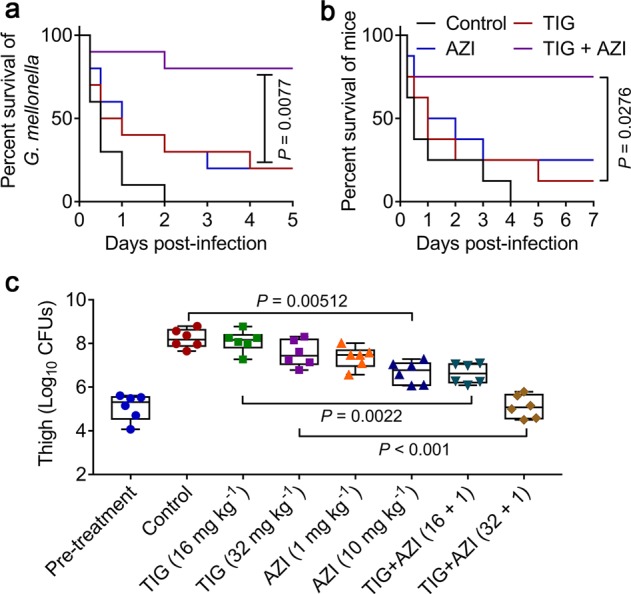
a, b In vivo synergy between tigecycline and azidothymidine in a G. mellonella larvae (a) and mouse peritonitis model (b). G. mellonella larvae (n = 10 per group) or CD-1 female mice (n = 8 per group) were infected with a lethal dose of E. coli B3-1. After 2 hours post infection, mice were treated with a single dose of PBS, tigecycline (32 mg kg−1), azidothymidine (1 mg kg−1) or combination of tigecycline (32 mg kg−1) plus azidothymidine (1 mg kg−1) by intraperitoneal injection. Survival of G. mellonella larvae and mice were recorded at 5- or 7-days post infection, respectively. P values were determined by log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test. c Bacterial burden of right thigh muscle in a neutropenic mouse thigh infection model by a nonlethal dose of E. coli B3-1 significantly decreased after a single intraperitoneal dose of combination treatment. P values were determined by Mann–Whitney U test.
