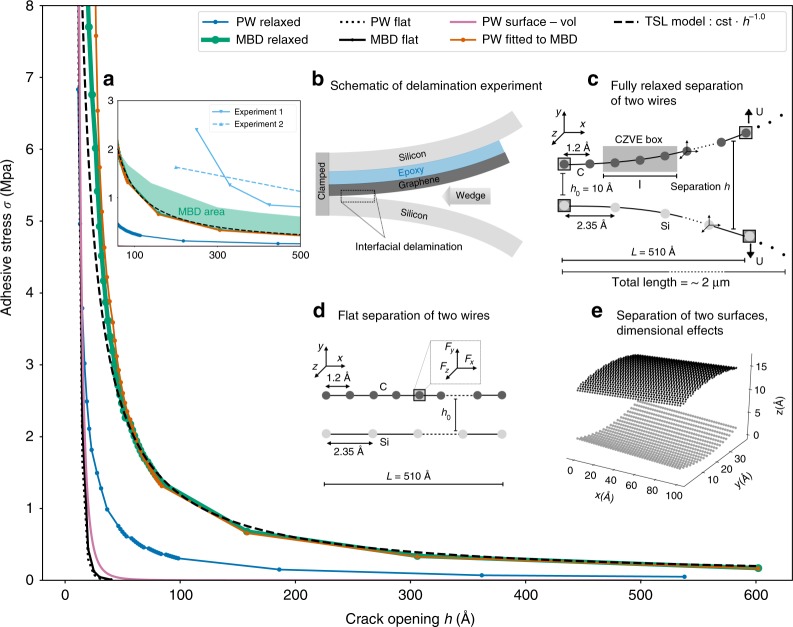
Fig. 1. Adhesive stress between carbon and silicon obtained with different methods.
Traction-separation law (TSL) calculated with numerical simulations with PW and MBD vdW interactions. The experimental setup for silicon/graphene/epoxy/silicon separation by using a test wedge, adapted from ref. 15 is schematically depicted in b. Three schematizations of the delamination model are proposed to study the adhesive interface: the first is based on flat separation (d), the second corresponds to the variationally optimized configuration (c), and the last scheme is an approximation of the relaxed geometry in 3D (e). Delamination along the y direction is accentuated in diagram (e) for clarity. In each scheme, both PW and MBD vdW approaches are adopted to describe nonbonded interactions. Atoms are separated by covalent bonds, which can be described by the pairwise harmonic potential. TSLs obtained numerically between graphene and silicon are plotted for the different models. Ultra-long-range interaction is found by variational optimization based on MBD interactions. Comparison with experimental data from ref. 15 is given in a. The MBD area indicates the sensitivity of MBD results with respect to the adopted damping parameters. The adhesive stress is computed exploiting the concept of cohesive zone volume element (CZVE), see details in “Methods” and Supplementary Note 3.