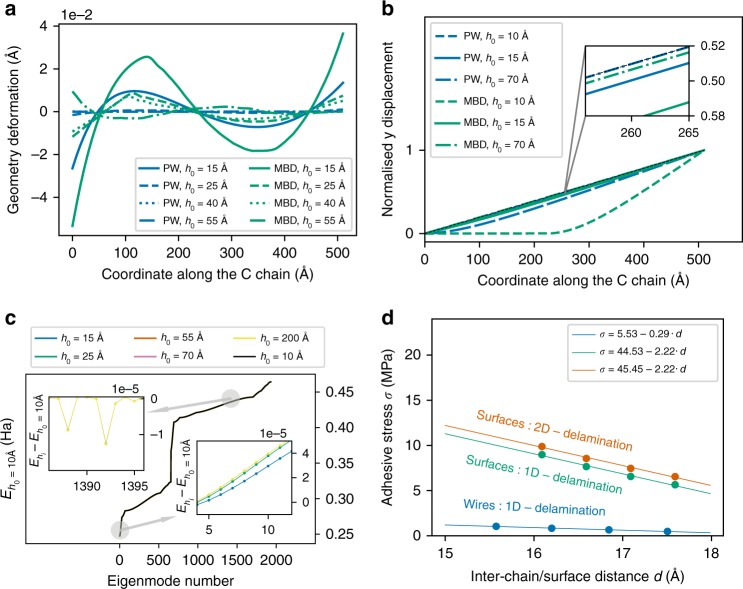
Fig. 2. Analysis of physical parameters influencing the adhesive stress.
a Secondary geometry deformations for different values of the interchain distance h0. Relaxed MBD geometries exhibit more pronounced deformations than those obtained from the PW model. MBD deformations slowly decrease at growing interchain distance, while the PW deformations quickly converge to zero for h ≥ 25 Å. b Carbon wires normalized y displacement in the relaxed geometry for different values of h0. Relaxed MBD geometries exhibit more significant non-linearities compared with PW. c Frequency spectrum of the collective electron-density oscillation modes, derived from the MBD Hamiltonian (plasmon dispersion) at various interchain distances h0. Frequency variation between a given interchain distance and h0 = 10 Å is reported for the lowest and highest energy mode intervals. d Adhesive stress as a function of the interchain/surface distance for three models with different dimensionality. Dimensional effects are clearly captured showing that the most complex 3D separation model (where both structures are allowed to delaminate in all directions) exhibits longer adhesive stress range and larger adhesive strength.