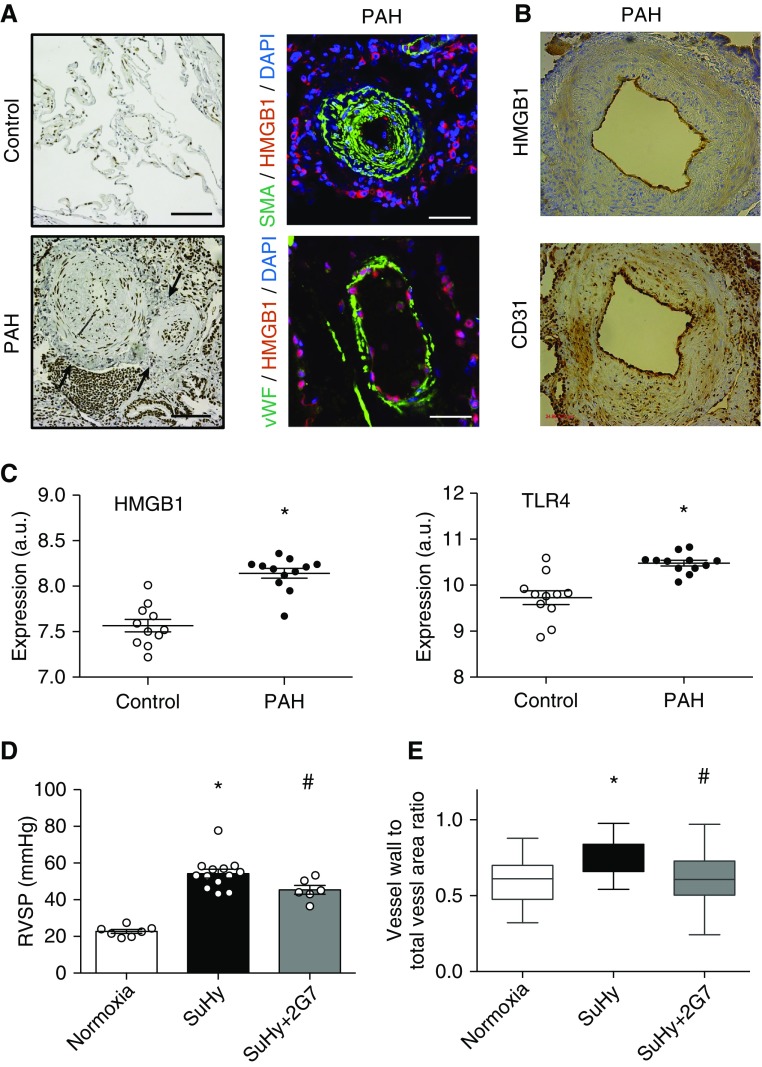
Figure 1.
HMGB1 (high-mobility group box-1) in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). (A) HMGB1 is upregulated in human PAH. Healthy lung tissue from patients with lung cancer at the time of resection (control) is devoid of high-intensity extracellular HMGB1 staining, whereas patients with PAH show elevated HMGB1 expression in pulmonary vessels and adventitial lymphoid tissue. Left panels depict HMGB1 staining, and right panels show immunofluorescence of SMA (smooth muscle actin) or vWF (von Willebrand factor) together with HMGB1. Note the cytosolic HMGB1 staining in the vascular adventitia, indicating activation and HMGB1 secretion (arrows). Scale bars, 100 μm. (B) Serial 4-μm sections showing colocalization of HMGB1 and CD31 in endothelial cells in a patient with PAH. (C) mRNA concentrations of HMGB1 and TLR4 (Toll-like receptor 4) are upregulated in lungs of patients with PAH compared with control lungs (*P < 0.001). (D) Right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) and (E) vessel wall thickness in pulmonary arterioles of normoxic (n = 7), Sugen/hypoxia (SuHy) isotype control antibody–treated (n = 13), and SuHy anti-HMGB1 antibody–treated (n = 6) rats. Anti-HMGB1 antibody or isotype control treatment started at the time of model induction. For histological analysis, at least 74 vessels were measured per treatment group. *P < 0.05 versus normoxia; #P < 0.05 versus isotype control antibody.