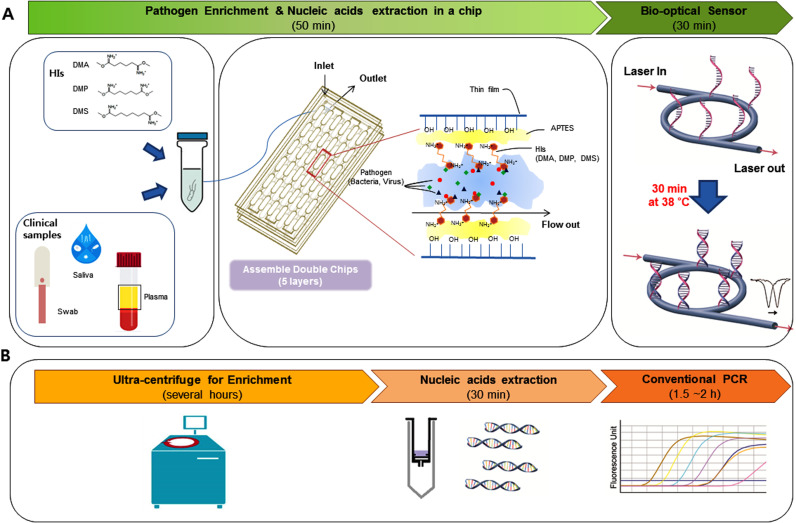
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the principle of ultrasensitive pathogen detection in clinical specimens. (A) Ultrasensitive pathogen detection system combining a simple and label-free system via homobifunctional imidoesters (HIs) with a microfluidic (SLIM) platform and an isothermal solid-phase nucleic acid amplification and detection sensor (iNAD). A mixture clinical sample and HI reagent is added to the SLIM system to enrich the pathogen and extract the DNA/RNA within 50 min without the need for detergents or bulky instruments. The extracted nucleic acids using the SLIM system were then used to detect a pathogen via an iNAD sensor. (B) Work flow of conventional methods for detection of pathogens with enrichment via ultracentrifugation, nucleic acid extraction on a column, and pathogen detection by real-time PCR.