Table 1.
Chemical structure and physico-chemical properties of the test compounds.a.
| Compound | R | Yield (%) | HPLCbRT | TLCcRf | Formula | Molecular weight |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculated | Measured MALDI-TOFd (M+Na)+ | |||||||
| Aglycones | ||||||||
| 1 | Me | 90 | 14.68 | (A) 0.62 | C53H52N8O17Cl2 | 1143 | 1165 | |
| 2 | H | 65 | 14.60 | (B) 0.26 | C60H51N7O19 | 1173 | 1196 | |
| Squaric acid amide esters | ||||||||
| 4 | Me | 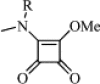 |
83 | 13.60 | (A) 0.73 | C58H54N8O20Cl2 | 1254 | 1275 |
| 5 | H | 60 | 36.51 | (D) 0.36 | C65H53N7O22 | 1284 | 1306 | |
| Asymmetric squaric diamides | ||||||||
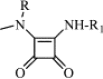 |
||||||||
| Compound | R | R1 | Yield (%) | HPLCbRT | TLCcRf | Formula | Molecular weight |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculated | Measured MALDI-TOFd (M+Na)+ | |||||||
| 7a | Me | —(CH2)5–CH2OH | 38 | 12.99 | (B) 0.13 | C63H65N9O20Cl2 | 1139 | 1160 |
| 8a | H | 72 | 13.06 | (B) 0.42 | C70H64N8O22 | 1369 | 1392 | |
| 7b | Me | —(CH2)5–COOH | 34 | 13.02 | (B) 0.12 | C63H63N9O21Cl2 | 1353 | 1374 |
| 8b | H | 38 | 13.03 | (B) 0.24 | C70H62N8O23 | 1383 | 1405 | |
| 8b1 | H | —(Gly)3–COOH | 62 | 10.90 | (A) 0.68 | C70H60N10O25 | 1441 | 1464 |
| 7c | Me | 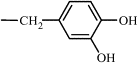 |
68 | 13.28 | (C) 0.29 | C65H61N9O21Cl2 | 1375 (3) | 1396 |
| 8c | H | 87 | ND | (B) 0.43 | C72H60N2O23 | 1405 | 1428 | |
| 8d | H | 73 | 16.68 | (B) 0.59 | C75H65N9O21 | 1428 | 1450 | |
| 7e | Me | 63 | 18.24 | (B) 0.44 | C70H63N9O19Cl2 | 1405 | 1426 | |
| 8e | H | 68 | 18.47 | (B) 0.53 | C77H62N8O21 | 1435 | 1457 | |
| 7f | Me | 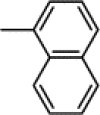 |
58 | 16.70 | (B) 0.28 | C67H59N9O19Cl2 | 1365 | 1386 |
| 8f | H | 54 | 16.75 | (B) 0.73 | C74H58N8O21 | 1395 | 1417 | |
| 7g | Me | 20 | 21.16 | (C) 0.60 | C75H65N9O19Cl2 | 1467 (65) | 1488 | |
| 8g | H | 42 | 21.21 | (C) 0.56 | C82H64N8O21 | 1496 | 1519 | |
| 8h | H | 62 | 19.31 | (B) 0.75 | C78H60N8O21 | 1445 | 1467 | |
| 8i | H | 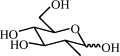 |
75 | 10.07 | (B) 0.34 | C70H62N8O26 | 1431 | 1454 |
| 8j | H | 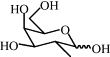 |
69 | 10.05 | (B) 0.35 | C70H62N8O26 | 1431 | 1454 |
After conversion of the aglycons aglycovancomycin (1) and aglycoristocetin (2) into their squaric acid amide esters (4 and 5, respectively), these were converted to the asymmetric squaric diamides (7a–g, derived from aglycovancomycin, and 8a–j, derived from aglycoristocetin).
HPLC conditions: instrument: Waters 600 with UV230nm detection; column: Lichrospher RP-8 (4 mm × 250 mm; 10 μm); injection volume: 20 μl (corresponding to 2 μg compound); solvents: (A) CF3COOH–H2O (pH 2.6) and (B) acetonitrile–H2O; gradient elution from 10 to 90% B; ND: not done.
TLC conditions: silicagel 60F25; solvent systems: (A) nBuOH–Pyr–AcOH–H2O (15:10:3:12); (B) toluene–MeOH–AcOH (1:1:0.01); (C) nBuOH–AcOH–H2O (4:2:2); (D) toluene–MeOH–AcOH (1:1:0.05).
MALDI-TOF MS: instrument: Brucker BIFLEX III. The analytes at a concentration of 5 mg per ml in acetontrile–H2O–0.1% HCOOH (50:50:0.1) were prepared with 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHB) matrix (20 mg/ml in DMSO).
