Fig. 2.
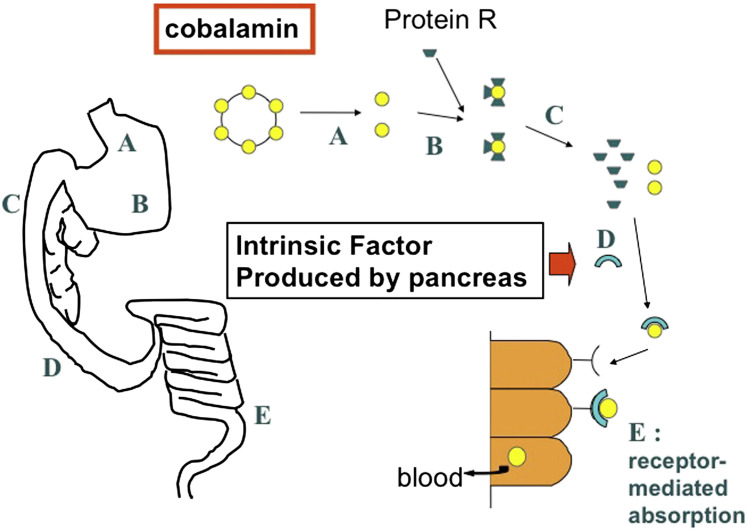
Absorption of cobalamin is a complex process involving several steps. Cobalamin is released from food protein in the stomach (A) and immediately bound to R-binder proteins (B). In the proximal small intestine, the cobalamin-R-binder complex is cleaved after digestion of the R-binder by pancreatic proteases (C). Free cobalamin can now bind to intrinsic factor (IF) (D), the majority of which is secreted by the pancreas in cats and dogs. This cobalamin-IF complex is subsequently absorbed by specialized receptors in the ileum (E).