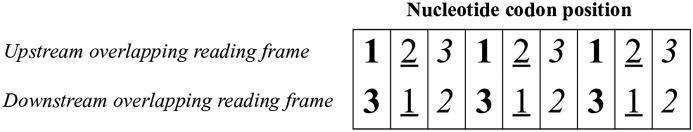
Fig. 1.
Orientation of overlapping genes, with the downstream frame having a shift of one nucleotide 3′ with respect to the upstream frame. There are 3 types of codon position (cp): cp13 (bold character), in which the first position of the upstream frame overlaps the third position of the downstream frame; cp21 (underlined character), in which the second position of the upstream frame overlaps the first position of the downstream frame; cp32 (italic character), in which the third position of the upstream frame overlaps the second position of the downstream frame. Based on the genetic code, a nucleotide substitution at first codon position causes an amino acid change in 95.4% of cases, at second codon position in 100% of cases, and at third codon position in 28.4% of cases. Thus, nucleotide substitutions at the codon positions “13” and “32” are usually non-synonymous in one frame and synonymous in the other. Nucleotide substitutions at the codon position “21” are almost all non-synonymous in both frames.