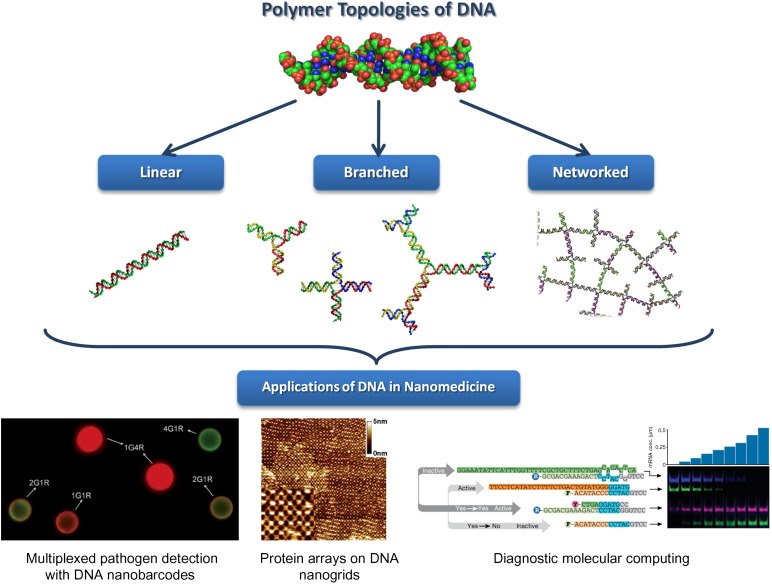
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustrating the assembly of DNA as a polymer with different topologies – linear, branched and networked – and how these topologies translate to applications in nanomedicine. Examples include multiplexed pathogen detection based on branched DNA (Figure reproduced from reference [119]), protein arrays assembled on DNA nanogrids (Figure reproduced from reference [137] with permission), and diagnostic molecular computing (Figure reproduced from reference [152] with permission).