Fig. 1.
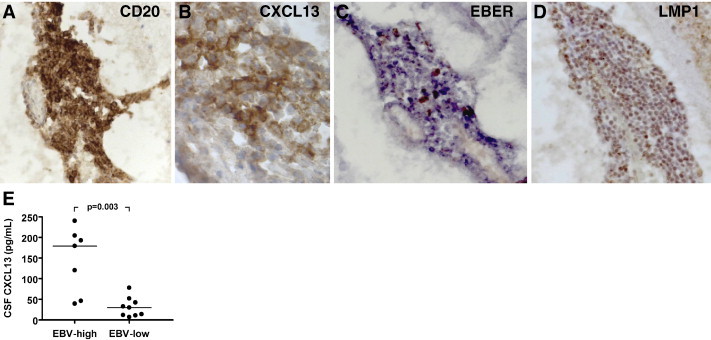
CXCL13 in MS ectopic B-cell follicles and CSF. Immunostainings for the pan B-cell marker CD20 (A) and for the lymphoid chemokine CXCL13 (B) were performed on serial brain sections from a case with secondary progressive MS, as previously described (Serafini et al., 2007). An intrameningeal B-cell follicle comprising numerous CD20+ B cells (A) aggregated around a network of CXCL13+ stromal cells/follicular dendritic cells (B) is shown. In situ hybridization for EBER (C) and immunostaining for the EBV latent protein LMP1 (D) (see Serafini et al., 2007 for staining protocols) reveal enrichment in EBV-infected cells inside the same B-cell follicle shown in A, B. Original magnifications: 250× in A, C and D, 1000× in B. Panel E shows the levels of CXCL13 protein in post-mortem CSF of MS cases that were classified as EBV-high (n = 7) and EBV-low (n = 9) based on the frequency of EBV-infected cells accumulating in the meninges and in white matter lesions (Serafini et al., 2007). The levels of CXCL13 are significantly higher in the CSF of MS cases characterized by more prominent deposits of EBV infection in brain tissue. CXCL13 levels were determined with a quantitative sandwich ELISA, in accordance with manufacturer's instructions (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA). Bars indicate median values. Between-group comparison was performed by Mann–Whitney test.
