Fig. 1.
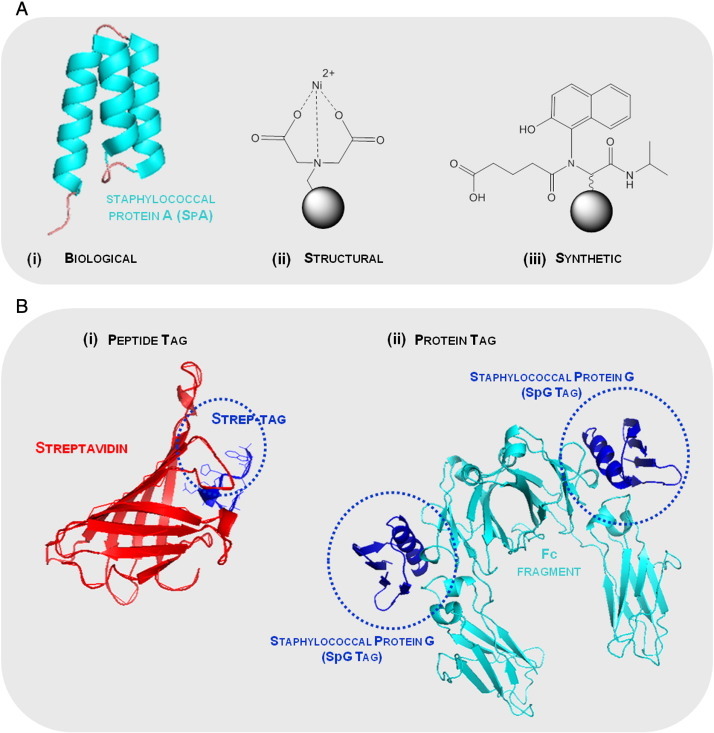
Examples of (A) affinity ligands and (B) peptide and protein affinity tags with their respective biological ligands employed on the purification of fusion proteins based on affinity chromatography. (A) The common affinity ligands can be (i) a biological ligand (staphylococcal protein A domain, PDB: 1DEE), (ii) a structural ligand (metal chelate such as iminodiacetic acid cheated to Ni2 +) and (iii) a synthetic biomimetic ligand (ligand A3C1 specific for immunoglobulins (Haigh et al., 2009). The solid support is representing agarose beads ( ). (B) The (i) peptide tag is the Strep-tag, an eight amino acid sequence, with the affinity for streptavidin protein (PDB: 1RST), whilst the (ii) example of a protein used as an affinity tag is related with the staphylococcal protein G and the respective biological ligand, immunoglobulin G (PDB: 1FCC).
). (B) The (i) peptide tag is the Strep-tag, an eight amino acid sequence, with the affinity for streptavidin protein (PDB: 1RST), whilst the (ii) example of a protein used as an affinity tag is related with the staphylococcal protein G and the respective biological ligand, immunoglobulin G (PDB: 1FCC).
