Fig. 4.
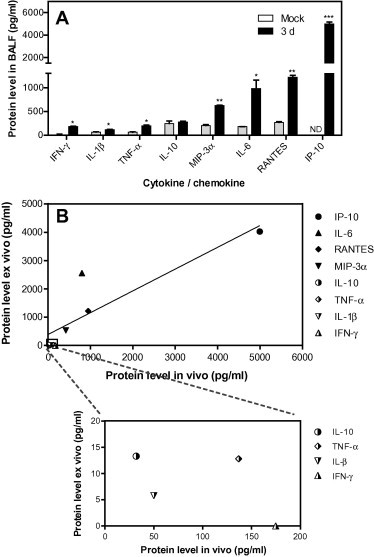
Correlation analysis of the cytokine and chemokine levels in response to influenza infection between the ex vivo and in vivo models. (A) The cytokine and chemokine levels in response to influenza infection in vivo. The bronchoalveolar lavage fluids (BALF) were subjected to cytokine and chemokine measurement by ELISA. Comparisons between infected mice and mock mice were performed by the unpaired t-test (*, 0.01 < p < 0.05; **, 0.001 < p < 0.01). The data are expressed as the means ± SEM. ND, not detected (the signal was below the detection limit of the commercial kit). (B) Comparison of the cytokine and chemokine levels in response to influenza infection between the ex vivo and in vivo models. After subtraction of the corresponding levels of the mock group, the correlation of the virus-induced IL-1β, IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-10, MIP-3α, IL-6, RANTES and IP-10 in BALF of day 3 post infection (Fig. 4A) and lung slice supernatants (Fig. 3C) were analysed by a linear regression analysis model.
