Fig. 5.
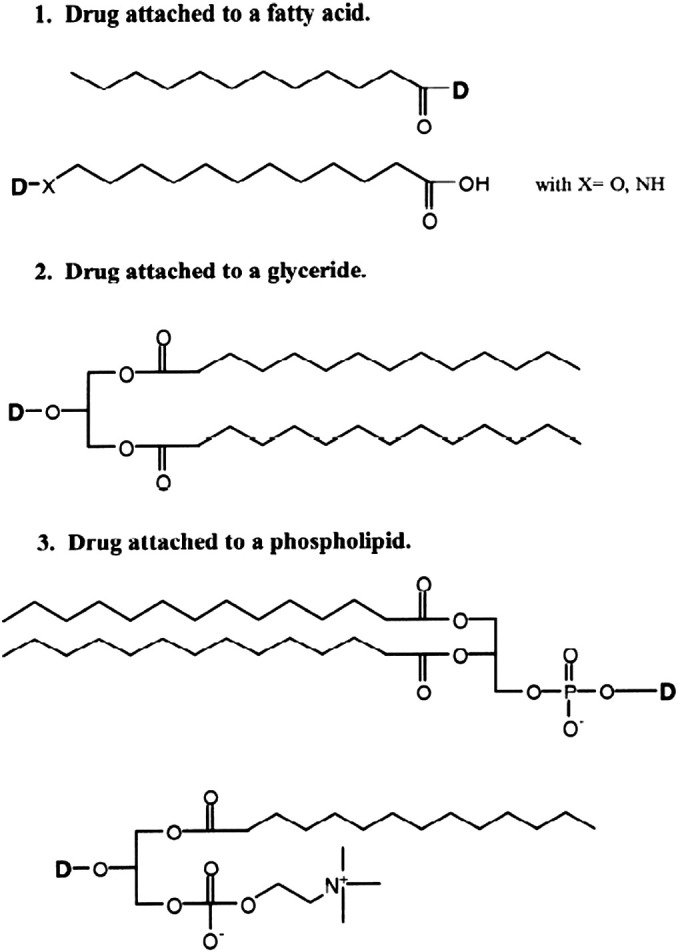
Types of lipidic carriers: fatty acids, glycerides and phospholipids. In the case of fatty acids, the drug is attached directly to the carboxylate or to a modified ω-atom. Drug-glycerides conjugates are represented here by a 1,3-diglyceride where the drug is in position-2. Phospholipid prodrugs consist either in drugs linked to the phosphate group or to the glycerol backbone, in this case, the drug replaces a fatty acid.
Reproduced from Lambert DM [249] with permission.
