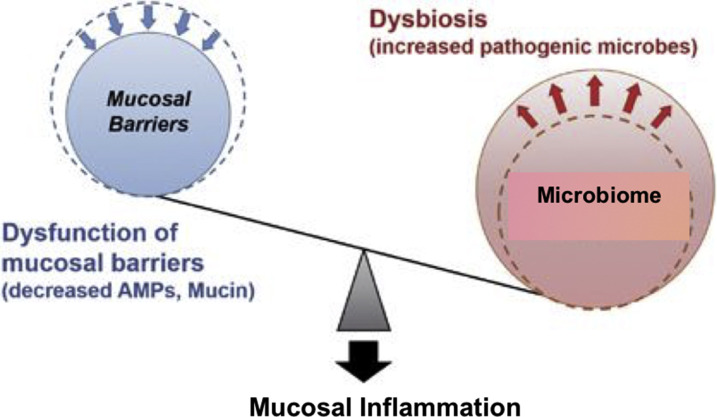
Fig. 9.
Microbial dysbiosis promotes susceptibility to mucosal inflammation. Dysfunction of mucosal barriers because of decreased production of AMPs and mucin allows intestinal bacteria to gain access to gut immune cells, thereby contributing to the development of intestinal inflammation. Dysbiosis induced by environmental factors, such as a high-fat diet and various antimicrobials and stressors, accelerates intestinal inflammation in situations where the mucosal barrier is disrupted.
(Adapted from Okumura R, Takeda K. Roles of intestinal epithelial cells in the maintenance of gut homeostasis. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(5):e338. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2017.20 with permission.)