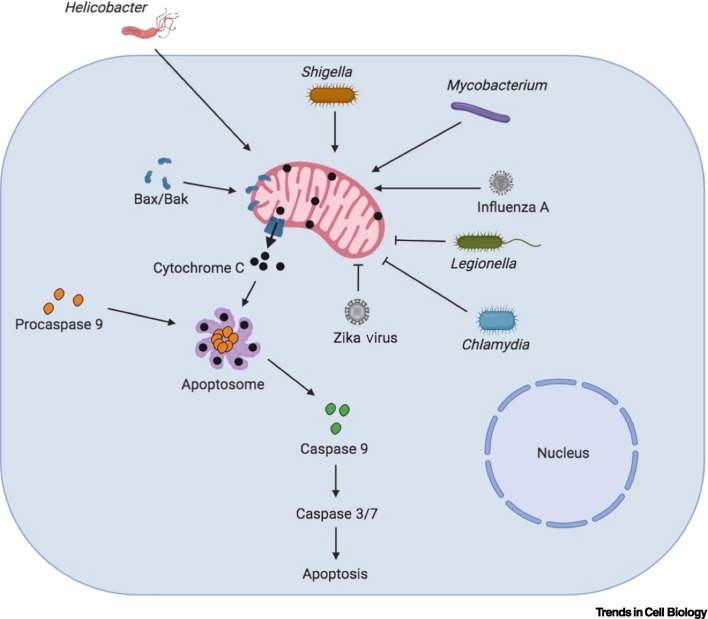
Figure 3.
Modulation of Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway upon Infection.
B cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) family proteins, including include Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax) and Bcl-2 homologous antagonist/killer (Bak), regulate the mitochondrial cell death pathway. Bax and Bak are proapoptotic proteins that localize to mitochondria and induce outer mitochondrial membrane permeabilization (MOMP), leading to the release of proapoptotic factors, such as cytochrome C, into the cytosol, which induce cell death by activating Caspases 9, 3, and 7 via the apoptosome complex. Bacteria and viruses influence this pathway and modulate the host response. Helicobacter, Shigella, and Mycobacterium infections lead to mitochondrial disruption that stimulates the mitochondrial apoptotic machinery and causes cell death. By contrast, bacteria such as Chlamydia and Legionella block the mitochondrial cell death pathway to promote their intracellular proliferation. Different viruses also exert varied effects on the mitochondrial cell death pathway. Influenza A enhances cell death, which helps in its dissemination, while Zika virus blocks cell death. Created with BioRender (www.BioRender.com).