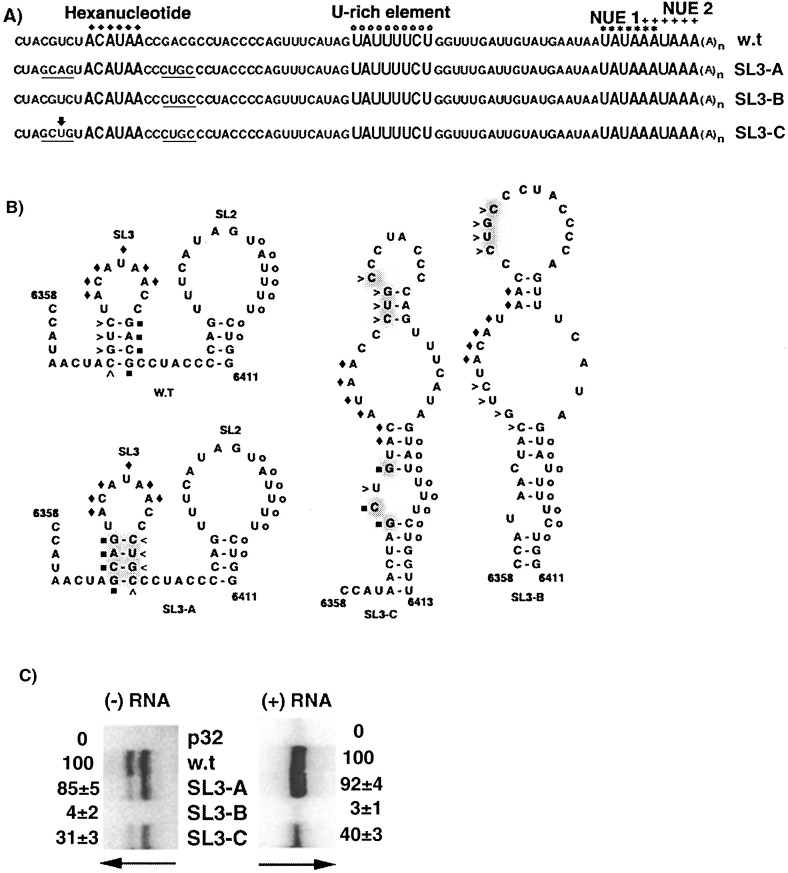
Figure 6.
Analyses of mutations predicted to affect SL3. (A) The 3′ NTR sequences of the wild-type and mutant transcripts are noted, with altered nucleotides underlined. (B) The predicted optimal secondary structures are depicted for wild-type and mutant RNAs between nucleotides 6358 and 6411. The wild-type sequence (CUGC) on the 5′ side of the SL3 stem is marked by arrowheads, and the wild-type sequence (GACG) on the 3′ side of the SL3 stem is indicated by filled squares. Alterations of these sequences are depicted by shading in the mutant structures. The hexanucleotide and U-rich elements are marked as in Figure 1. (C) Protoplasts inoculated with replication-defective transcripts (p32), wild-type (w.t.), and mutant transcripts (SL3-A, SL3-B and SL3-C) were analyzed for RNA accumulation as described in the legend to Figure 5(B).