Fig. 6.
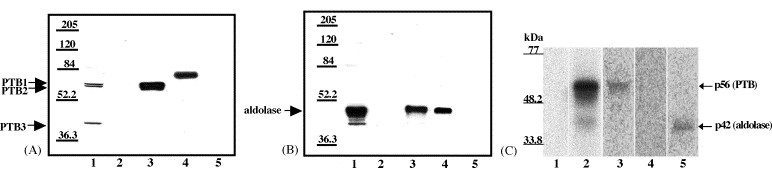
Confirmation of the identity of p56 and p42. (A) Western blotting analysis of RNA affinity chromatography eluate fractions using anti-PTB antibody. (Lane 1) original S100 extract (10 μl of 5 ml); (lane 2) 0.2 M NaCl wash (10 μl of 300 μl); (lane 3) 3 M NaCl eluate (10 μl of 300 μl); (lane 4) recombinant His-PTB (36 ng); (lane 5) mock column 3 M NaCl eluate (10 μl of 300 μl). (B) Western blotting analysis of RNA affinity chromatography eluate fractions using anti-aldolase antibody. (Lane 1) original S100 extract (10 μl of 5 ml); (lane 2) 0.2 M NaCl wash (10 μl of 300 μl); (lane 3) 3 M NaCl eluate (10 μl of 300 μl); (lane 4) purified aldolase (33 ng); (lane 5) mock column 3 M NaCl eluate (10 μl of 300 μl). (C) Immunoprecipitation of proteins cross-linked to SHFV 3′(+)NCR RNA. Scaled up UV-induced cross-linking reactions (90 μl) using cytoplasmic extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation with various antibodies. (Lane 1) free probe (only one-third of reaction volume was loaded onto the gel); (lane 2), UV-induced cross-linking reaction (only one-third of the reaction volume was loaded onto the gel); (lane 3) immunoprecipitation with anti-PTB antibody; (lane 4) immunoprecipitation with anti-hnRNP A1 antibody; (lane 5) immunoprecipitation with anti-aldolase antibody. The precipitate from the entire reaction volume was loaded onto the gel in lanes 3–5. Standard protein markers are indicated on the left.
