Fig. 1.
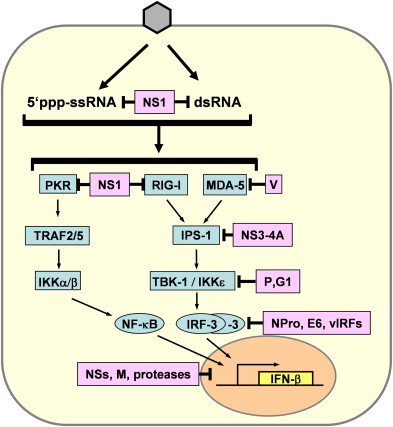
Viral inhibition of IFN induction. Intracellular recognition of 5′-triphosphorylated ssRNA and dsRNA by the intracellular receptors PKR, RIG-I and MDA-5 leads to activation of the transcription factors NF-κB and IRF-3 via several intermediate signaling factors. IRF-3 is phosphorylated by the kinases TBK-1 and IKKɛ which in turn are activated by RIG-I and MDA5 via IPS-1. NF-κB is mainly activated by the PKR pathway. Examples of viral IFN antagonists interfering with different steps in the IFN induction pathways are the NS1 of influenza viruses, the V protein of paramyxoviruses, the NS3-4A protein of hepatitis C virus, the P protein of Rabies virus, the G1 protein of hantavirus NY-1, the NPro protein of classical swine fever virus and bovine viral diarrhea virus, the E6 protein of human papilloma virus 16, the viral IRF homologs (vIRFs) of human herpes virus 8, the NSs proteins of bunyaviruses, the M protein of vesicular stomatitis virus, and the proteases of Picornaviruses.
