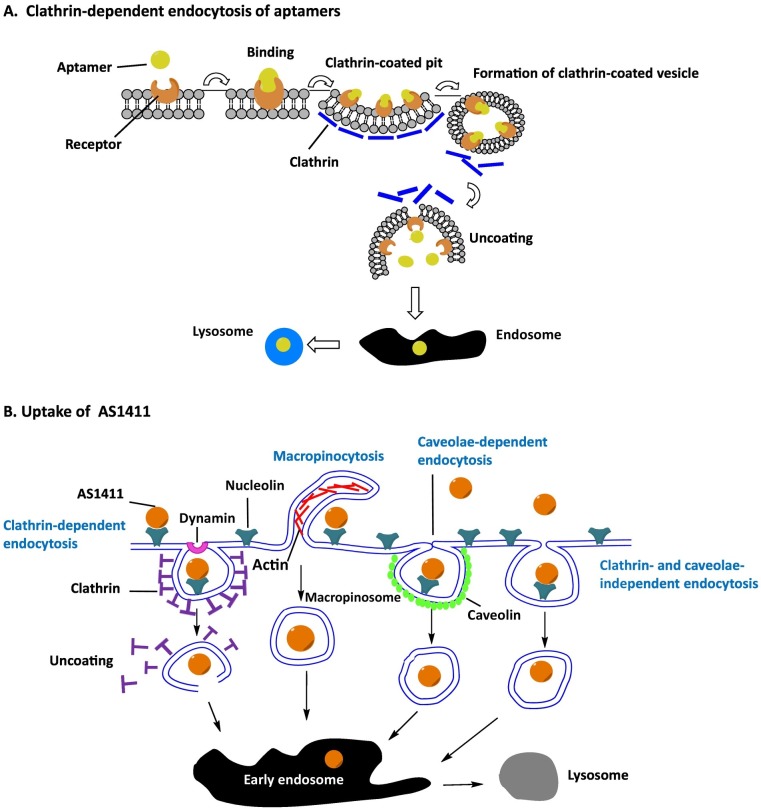
Fig. 1.
Mechanisms of endocytosis. (A) Clathrin-dependent endocytosis of aptamers. The binding of the aptamer and receptor initiate formation of the clathrin-coated pit, followed by clathrin-coated vesicle budding. Once detached from the membrane, the clathrin coat is disassembled. Clathrin-dependent endocytosis ends in fusion with endosomes and lysosomes. (B) Uptake mechanism of AS1411. The endocytosis of AS1411 involves multiple pathways. Although macropinocytosis is the predominant endocytosis mechanism of AS1411, clathrin- and caveolae-dependent and clathrin- and caveolae-independent pathways are all involved in uptake of AS1411.