Table 2.
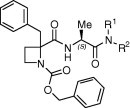
| Compd | R1, R2 | EC50 (μM) | Cytotoxicity (μM) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCMVa | MCCb | CC50c | ||
| (S,S)-4a | H, C(CH)3 | 45 | >100 | >100 |
| (R,S)-4a | H, C(CH)3 | 49 | >100 | >100 |
| (S,S)-4b | H, CH2Ph | >20 | 100 | 42 |
| (R,S)-4b | H, CH2Ph | >4 | ⩾20 | 42 |
| (S,S)-4c | H, CH2CH(CH3)2 | 63 | >100 | >100 |
| (R,S)-4c | H, CH2CH(CH3)2 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| (S,S)-4d | H, Chx | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| (R,S)-4d | H, Chx | >20 | 100 | 46 |
| (S,S)-4e | CH3, CH3 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| (R,S)-4e | CH3, CH3 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| (S,S)-1 | H, H | 32 | >50 | 50 |
| 11 | Z-Phe-Ala-NH2 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 12 | Z-Phe-Ala-NHtBu | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| GCV | 7.0 | ⩾1575 | 580 | |
Effective concentration required to reduce virus plaque formation by 50% (Davis strain). Virus input was 100 plaque forming units (PFU).
Minimum cytotoxic concentration that causes a microscopically detectable alteration of cell morphology.
Cytotoxic concentration required to reduce cell growth by 50%.
