Figure 2.
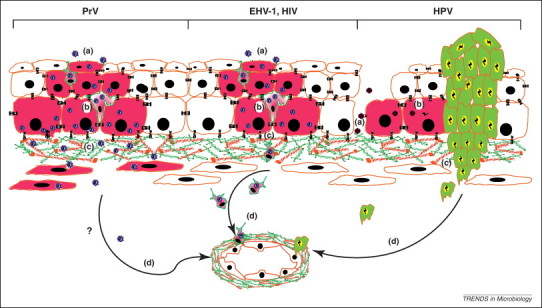
Different viral interactions with the BM. (a) Before entry into cells, viruses either attach directly to cell surface receptors (e.g. herpesviruses) or via intermediate binding to an exposed BM component in epithelial microlesions (e.g. human papillomavirus, HPV). (b) Viral replication and local dissemination (infected cells are in pink). Local immune cells may be infected (e.g. herpesviruses and HIV). (c) Viruses gain access to the stroma by breaching the BM. This may happen in a protease-mediated way (e.g. pseudorabies virus, PrV), via hijacking of immune cells to transverse the BM [e.g. equine herpesvirus 1 (EHV-1) and HIV] or via viral-driven metastasis out of a viral-induced tumor (e.g. HPV, green cells). (d) Finally, viruses may spread in the host by reaching blood or lymph vessels.
