Fig. 1.
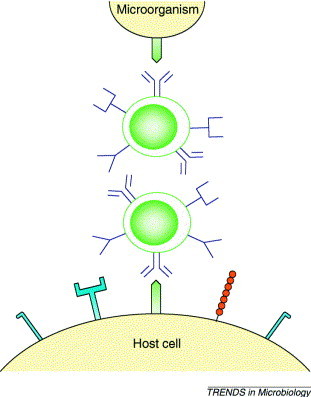
Molecular mimicry. Molecular mimicry occurs when a microorganism and its host share an immunological epitope. Infection with a virus having molecular mimicry (a cross-reacting determinant) with a self epitope could lead to an autoimmune response. Cross-reacting antibodies are known to react with conformational as well as linear epitopes and, more recently, it has been described that cross-reacting T cells recognize not only linear epitopes but also epitopes having similar conformations presented by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules.
