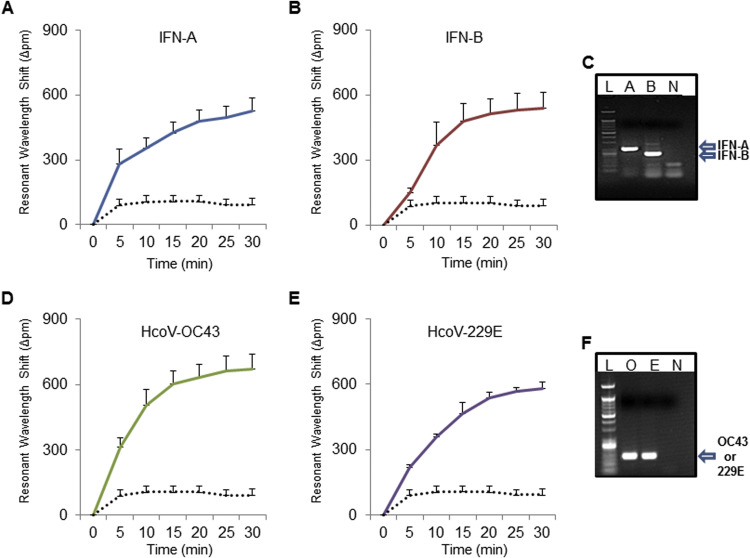
Fig. 2.
iROAD assay optimization. Resonance wavelength shift using the iROAD assay shows the results of viral RNA amplification/detection in a label-free and real-time manner. (A, B) Resonance wavelength shift shows the result of the amplification/detection of influenza (IFN)-A (blue), B (dark red), and negative control (black dot). Error bars indicate standard deviation from the mean, based on at least 3 independent experiments. (C) Gel electrophoresis data for end-point reverse transcription (RT)-PCR product from IFN-A and B. (D, E) Resonance wavelength shift shows the amplification of human coronavirus (HCoV)-OC43 (green), HCoV-229E (purple), and negative control (black dot). (F) Gel electrophoresis data for end-point reverse transcription (RT)-PCR product from HCoV-OC43 and HCoV-229E. Error bars indicate standard deviation from the mean, based on at least 3 independent experiments. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)