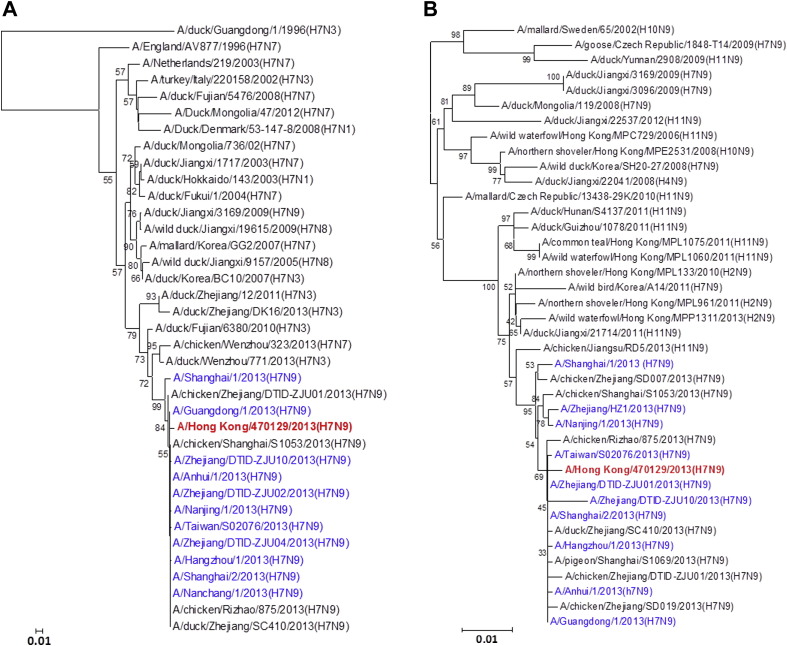
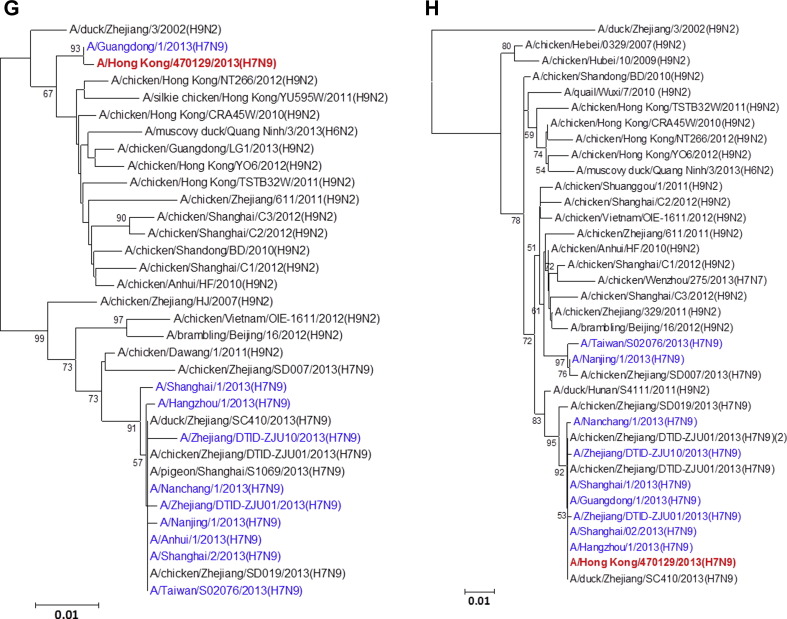
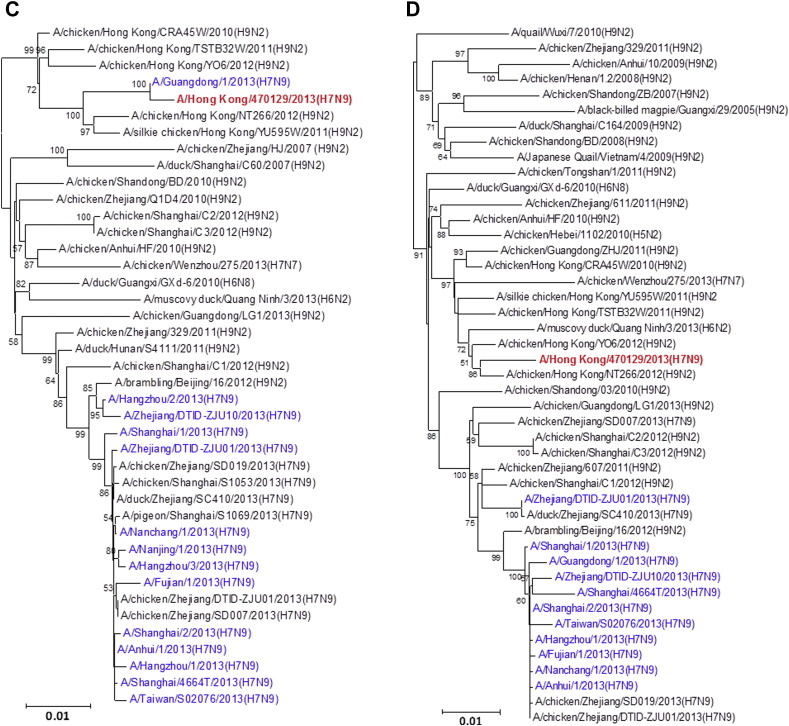
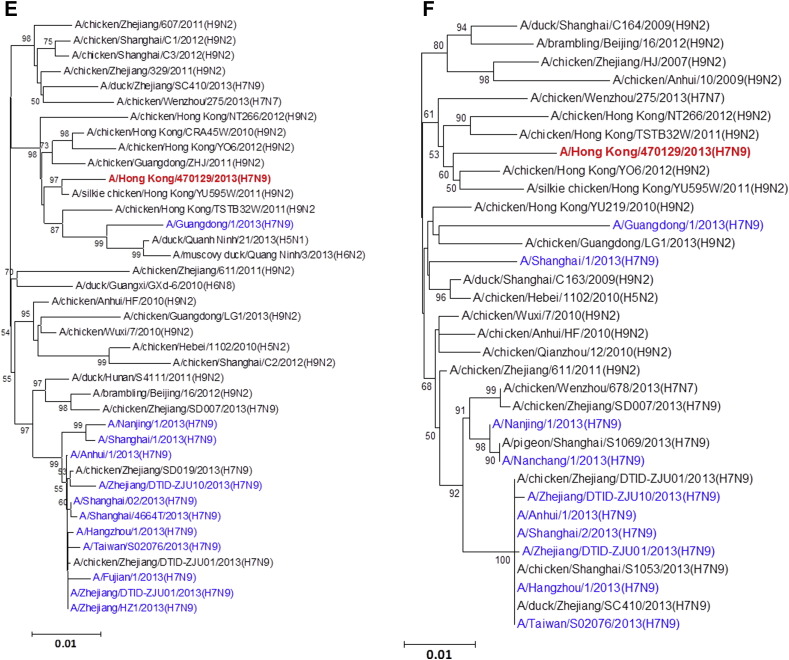
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic trees showing the relationship of A/Hong Kong/470129/2013 to other A(H7N9) and non-A(H7N9) avian influenza viruses. (A) HA1. (B) NA. (C) PB2. (D) PA. (E) PB1. (F) NP. (G) NS. (H) MP. The phylogenetic trees were constructed using neighbour-joining method with Tamura-Nei model of nucleotide substitution using MEGA software package, version 5.05. The bootstrap values from 1000 replicates were performed to evaluate the reliability of the phylogenetic trees. The A/Hong Kong/470129/2013 was highlighted in bold font in red, while other human A(H7N9) strains were highlighted in blue. Sequences not determined in this study were obtained from NCBI Influenza Virus Resource database, except A/Anhui/1/2013 and A/Shanghai/1/2013 which were obtained from Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data (GISAID) EpiFlu™ Database (Supplementary Table).