Table 2.
Synthetic or natural derivatives of lycorine and their anticancer activity compare to lycorine.
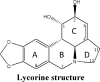 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Position | Substitution or derivate | Activity | Ref |
| Ring-A | Open dioxole | Moderately active | [23] |
| Open dioxole with absence of -OH at C2 | Inactive | [23] | |
| Ring-B | C7-oxidation, aromatic C-ring | Inactive | [23,133] |
| C7-oxidation | Decrease | [133] | |
| C7-thiol | Inactive | [133] | |
| Quaternization of N | Inactive | [23] | |
| Ring-C | 1-acetyl | Decrease | [23,134,135] |
| 1-acetyl, 2-silyl | Inactive | [134] | |
| 1-alkyl, 2-silyl ether | Moderately active | [86,135] | |
| 1-silyl, 2-alkyl ether | Inactive | [86,134] | |
| 2-amines | Decrease | [136] | |
| 2-β acetyl | Inactive | [23] | |
| 2-epoxide | Increase | [136] | |
| 2-esters | Decrease | [136] | |
| 2-methoxy | Equipotent | [23,134] | |
| 1 or 2 methyl ether | Inactive | [86] | |
| 1 or 2 benzoate | Equipotent | [133] | |
| 1, 2-diacetyl | Inactive | [23,134,135] | |
| 1, 2-dicarbonate | Equipotent | [133] | |
| 1, 2-diether | Decrease | [86] | |
| 1,2-dipropionate | Equipotent | [133] | |
| 1,2-disilyl | Inactive | [134] | |
| 1,2,3,4-tetraol | Inactive | [133] | |
| 2.3-diallyl | Equipotent | [133] | |
| Aromatic C ring | Selective | [23] | |
| Oxiadation of C3-C4 double bond | Inactive | [23,136] | |
| Steriochemistry change | Inactive | [23] | |
| Ring-D (narciclasine type) | Narciclasine | Equipotent | [135,137] |
| Narciclasine tetraacetate | Equipotent | [135] | |
| C10b-R-hydroxypancratistatin | Moderately active | [135] | |
| Cis-dihydronarciclasine | Moderately active | [135] | |
| Trans-dihydronarciclasine | Decrease | [135] | |
| Ring-D (crinine type) | Haemanthamine | Equipotent | [135] |
| Buphanamine | Inactive | [135] | |
| 11-hydroxyvittatine | Inactive | [135,138,139] | |
| Natural derivatives | Pseudolycorine | Moderately active | [23,135] |
| Amarbellisine | Moderately active | [135] | |
| Ungeremine | Inactive | [23,135] | |
| Norpluiine | Inactive | [23,135] | |
| Lycorene | Inactive | [23] | |
