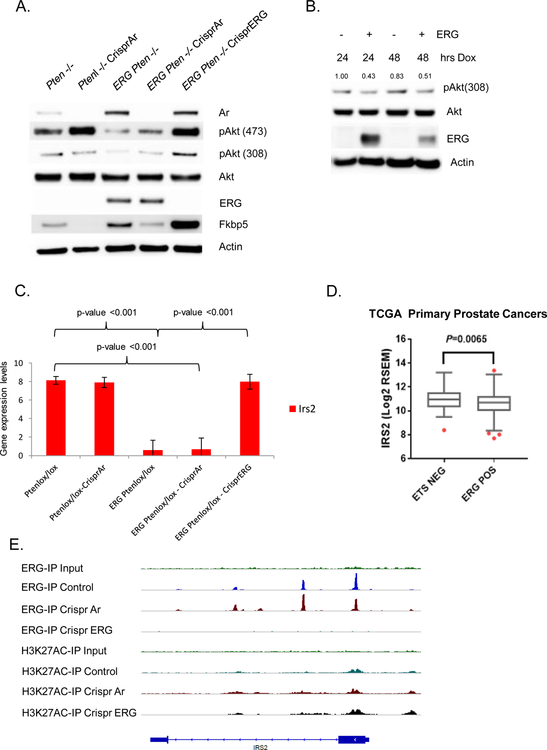
Figure 2. PI3K repression is ERG dependent and ERG suppresses IRS2 transcriptionally.
A) Using the Crispr/Cas9 technology, AR and ERG were knocked-out from our Pten−/− and Rosa26-ERG Pten−/− prostate organoids and protein lysates were analyzed by western blotting. As predicted, knock-out of AR in the setting of Pten loss robustly activated PI3K signaling. Surprisingly though knock-out of AR in the setting of ERG expression had minimal effect on PI3K signaling, while knock-out of ERG increased pAkt levels profoundly (experiment run in triplicate). B) Acute doxycycline induced overexpression of ERG in wild-type prostate organoids versus vector control demonstrated repression of PI3K signaling correlated with ERG expression levels (experiment run in triplicate, quantification of pAkt normalized to actin and Akt). C) mRNA expression of IRS2 was significantly repressed by ERG in our prostate organoids. Three independent lines for each genotype were analyzed with error bars reporting standard deviation from the mean. D) Analysis of IRS2 expression in the TCGA data set reveals that prostate cancers harboring ERG genomic rearrangements have a significantly repressed IRS2 expression. E) ChIP seq analysis demonstrates that ERG binds to the transcription start site of IRS2.