Figure 6. P-AscH− treatment increases DUOX1 and DUOX2 expression in vivo.
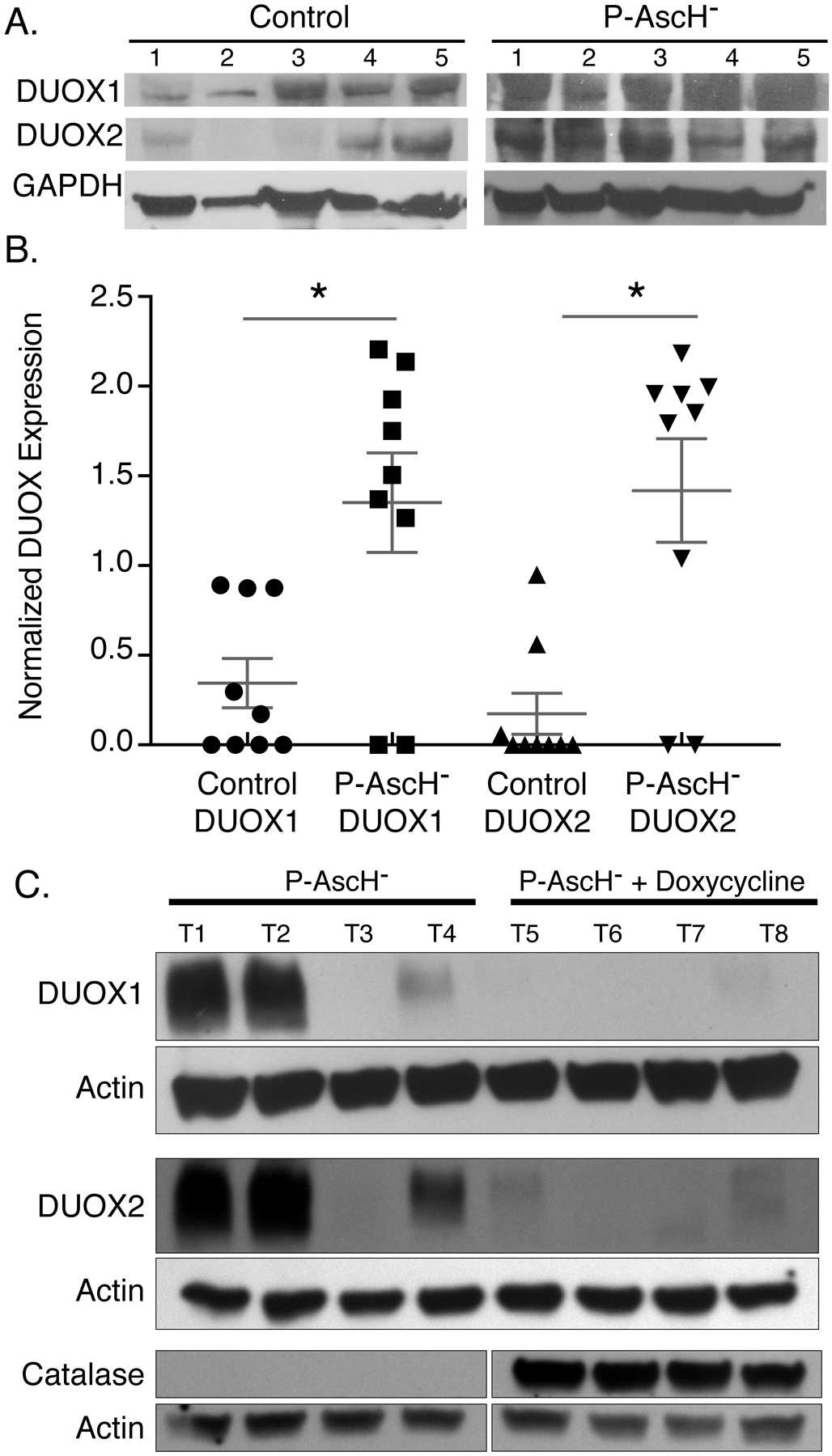
A. Athymic nude mice with heterotopic MIA PaCa-2 xenografts were treated for 5 days with 4 g/kg I.P. ascorbate b.i.d. Western blotting was performed to analyze protein levels of DUOXs in xenograft tumors that were excised from control and P-AscH− treated mice. DUOX1 and DUOX2 immunoreactive protein is increased in tumors of P-AscH− treated mice compared to saline treated mice (Representative blots shown).
B. Quantification of densitometric evaluation of western blots (Means ± SEM, n = 9, * p < 0.05 vs. controls, 2-tailed student’s t-test).
C. Athymic nude mice with heterotopic H1299T-CAT xenografts were treated for 5 d with 4 g/kg I.P. ascorbate b.i.d. All mice were given 1% sucrose in their drinking water ± doxycycline (2 mg/mL). Tumors were excised, and western blotting was performed to analyze protein levels of DUOXs and catalase in xenografts. DUOX1 and DUOX2 immunoreactive protein is increased in tumors of P-AscH− treated mice compared to mice in the P-AscH− + doxycycline group. Catalase immunoreactive protein is increased in tumors from the P-AscH− + doxycycline group compared to the P-AscH− group. (Representative blots shown, n = 4 mice per group).
