Figure 2.
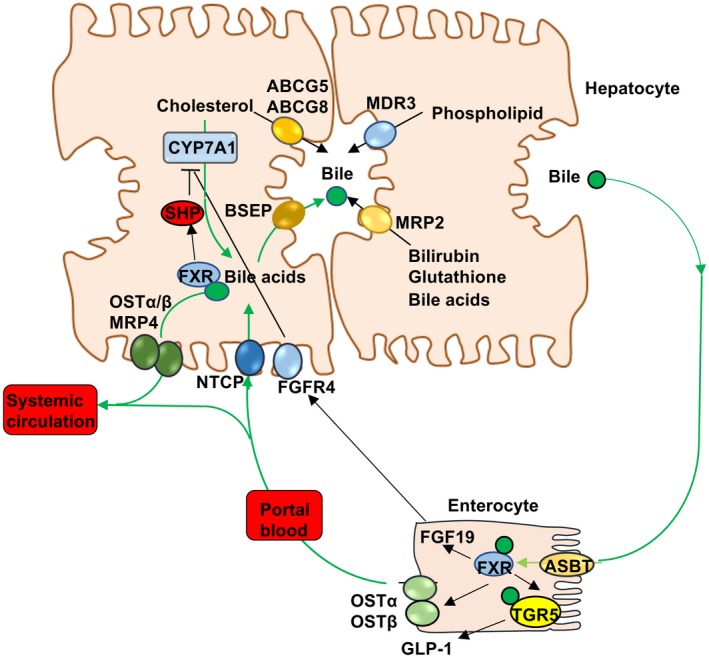
FXR regulation of bile acid synthesis and enterohepatic circulation of bile acids. In hepatocytes, FXR induces SHP, which inhibits transcription of CYP7A1 and bile acid synthesis. FXR induces BSEP, which actively excretes bile acids into bile. Bile acids also facilitate biliary cholesterol secretion via ATP binding cassette family G5 and G8 transporters (ABCG5, ABCG8). MDR3 (ABCB4) transports phospholipids into bile, whereas MRP2 transports bilirubin, glutathione, and unconjugated bile acids. In the ileum, bile acids are reabsorbed into enterocytes via ASBT. Intestinal FXR induces sinusoidal OSTα/OSTβ heterodimer to efflux bile acids into the portal blood circulation to the liver, where NTCP takes up bile acids into hepatocytes. Intestinal FXR induces FGF19, which circulates to the liver and binds to hepatic FGFR4, inhibiting bile acid synthesis. Bile acids also activate FXR to induce OSTα/OSTβ and MRP4 to efflux bile acids as an adaptive response to cholestasis. FXR induces TGR5 expression in enteroendocrine cells to stimulate secretion of glucagon‐like peptide 1 (GLP‐1), which stimulates insulin secretion from the pancreas and improves insulin sensitivity, and also promotes adipose tissue browning and energy metabolism.
