Fig. 3.
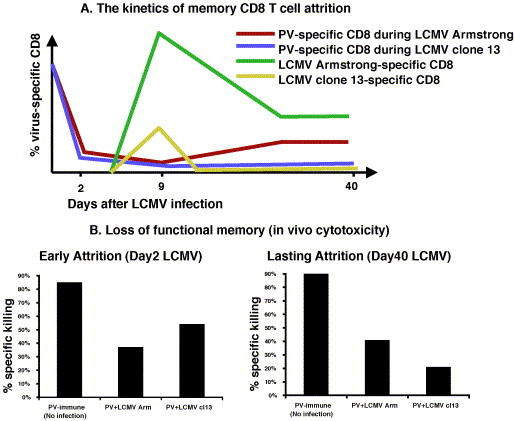
(A) The kinetics of non cross-reactive PV-specific memory CD8 T cell attrition demonstrates an ongoing loss of memory during heterologous persistent LCMV infection as compared to acute LCMV infection. PV-immune mice were infected with either acute LCMV Armstrong (red) or persistent clone13 (blue) infection. The frequency of dominant PV NP38-specific CD8 T cells in PBL was followed using IFNγ assay. The kinetics of attrition was overlaid with the kinetics of LCMV-specific CD8 T cell to show early depletion of PV-specific CD8 T cells. (B) Loss of functional PV-specific memory at the early and the late phase of LCMV infection as measured by an in vivo cytotoxicity assay. Using PV NP38-coated targets in PV-immune, PV-immune acutely infected with LCMV Armstrong or PV-immune mice infected with LCMV clone 13, which establishes a persistent infection, there is evidence for loss of functional memory both at the early phase (day 2) and the late phase (day 40) of LCMV infection with either LCMV strain [103].
