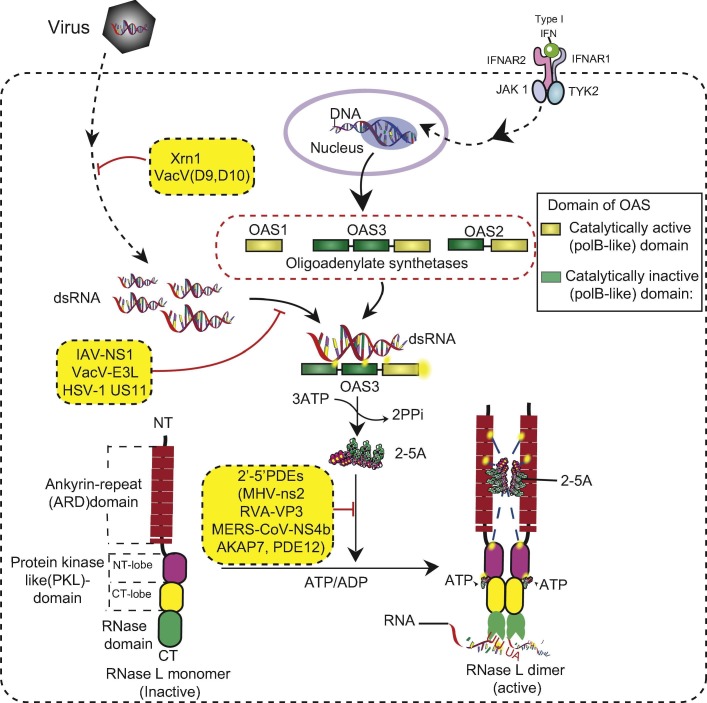
Fig. 1.
The OAS–RNase L pathway. The OAS-RNase L pathway is activated by dsRNAs and IFN signaling. Among the OASs, OAS3 senses dsRNA more efficiently and induces the synthesis of 2-5A from ATP. 2-5A then binds to the RNase L monomer and activates its dimer formation, which is the active conformation of RNase L. Active RNase L degrades cellular and viral RNA, leading to the restriction of virus replication. Several cellular and viral proteins inhibit the OAS-RNase L pathway at different stages.