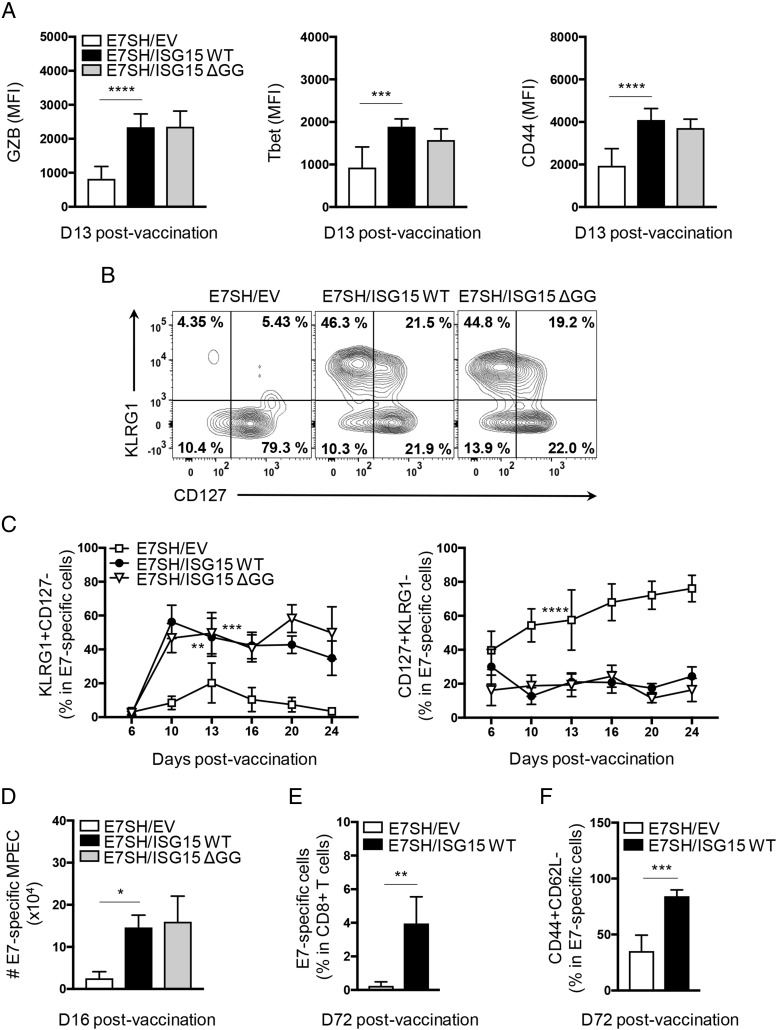
FIGURE 4.
The free form of ISG15 supports short-lived effector and effector memory differentiation of CTLs. (A–D) Mice (n = 7 per group) were vaccinated with plasmid encoding E7SH, either combined with EV, ISG15 WT, or ISG15 ΔGG as outlined in Fig. 2. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of protein expression as assessed by mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of GZB, Tbet, and CD44 on E7-specific CD8+ T cells in blood at day 13 postvaccination. (B) Representative flow cytometric analysis of E7-specific CD8+ T cells stained with Abs to KLRG1 and CD127. Numbers indicate percentage of cells in each quadrant. (C) Quantification of percentage of SLECs (KLRG1+CD127−) (left) and MPECs (CD127+KLRG1−) (right) within E7-specific CD8+ T cells in blood over time. (D) On day 16, three mice per group were sacrificed, and total numbers of CD127+KLRG1− E7-specific cells per spleen were determined. (E) Quantification of the percentage of E7-specific cells within CD8+ T cells in blood on day 72. (F) Quantification of the percentage of CD44+CD62L− cells among E7-specific CD8+ T cells in blood on day 72. Results are representative of two experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey posttest (A–D) or two-tailed Student t test (E). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.